Last update images today Southeast Asias Geographic Tapestry: A Guide
Southeast Asia's Geographic Tapestry: A Guide
Southeast Asia is a region brimming with cultural richness and breathtaking landscapes. Understanding its geography is key to appreciating its diversity and complexity. This article dives into the fascinating geography of Southeast Asia, exploring its key features, influences, and impact on the region's people and environment. We'll look at the trending aspects surrounding mapping and geographic data in the region, focusing on its importance this season.
Target Audience: Students, travelers, geography enthusiasts, researchers, and anyone interested in learning more about Southeast Asia.
1. Unveiling the Southeast Asia Geography Map: An Overview
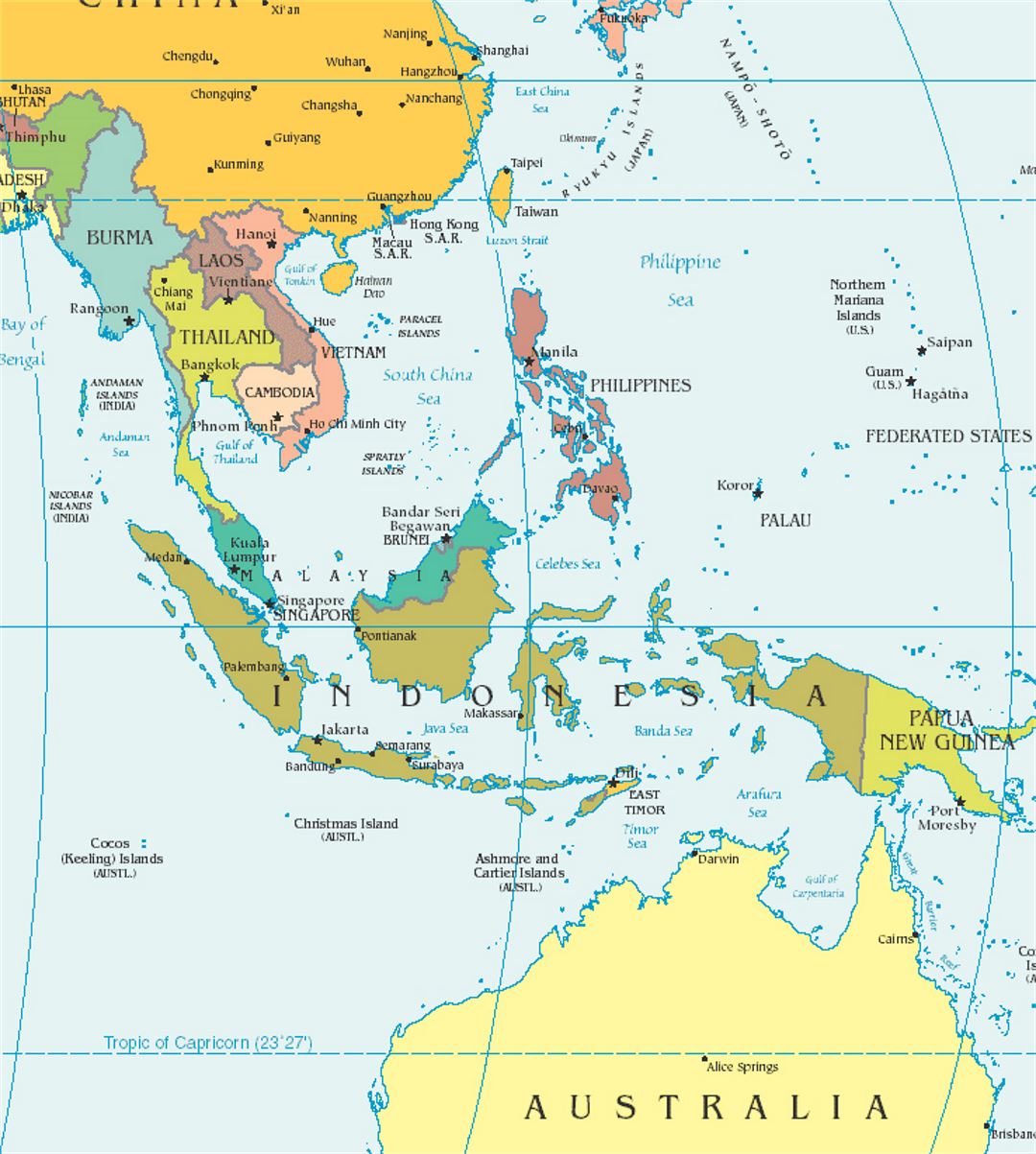
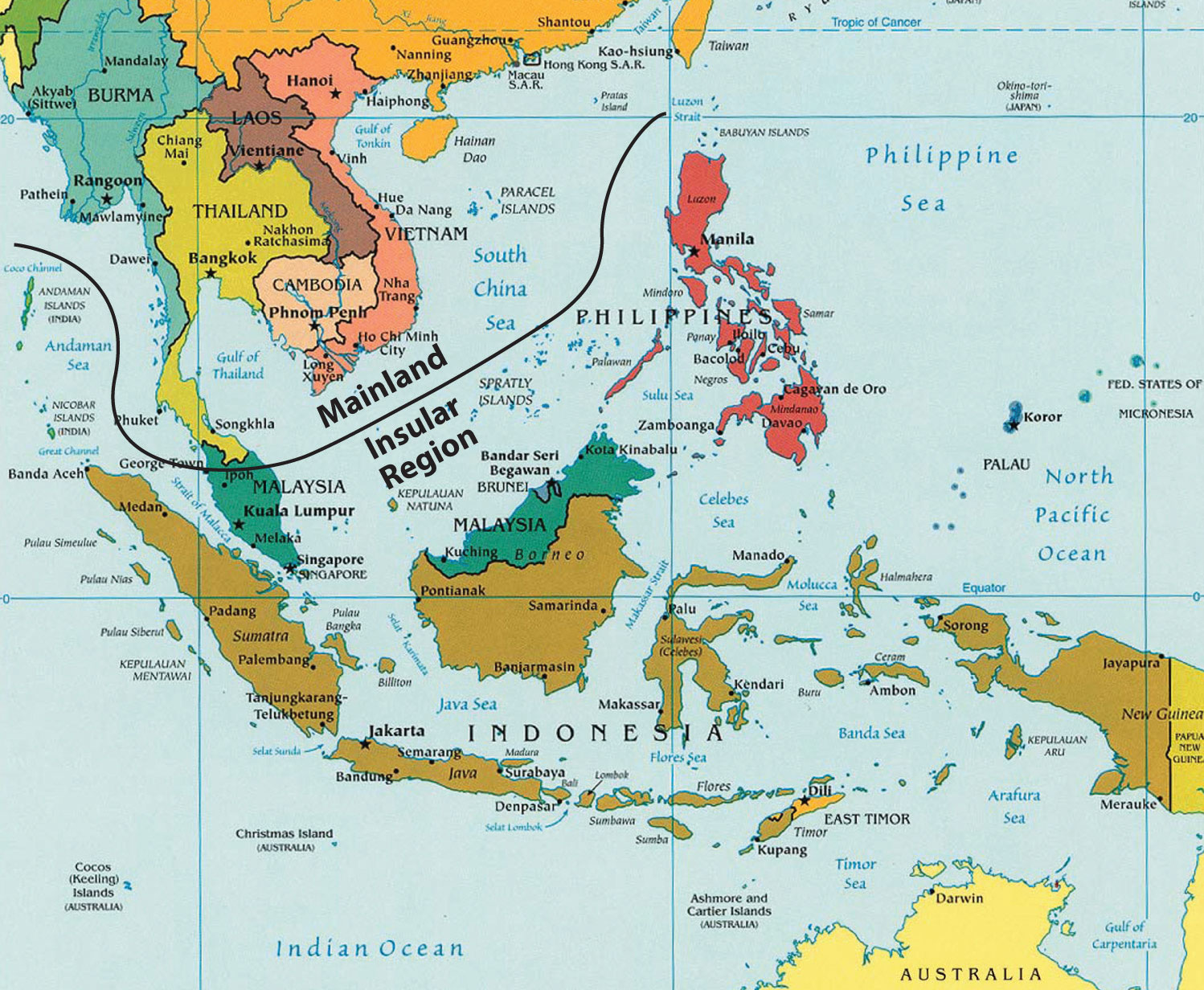
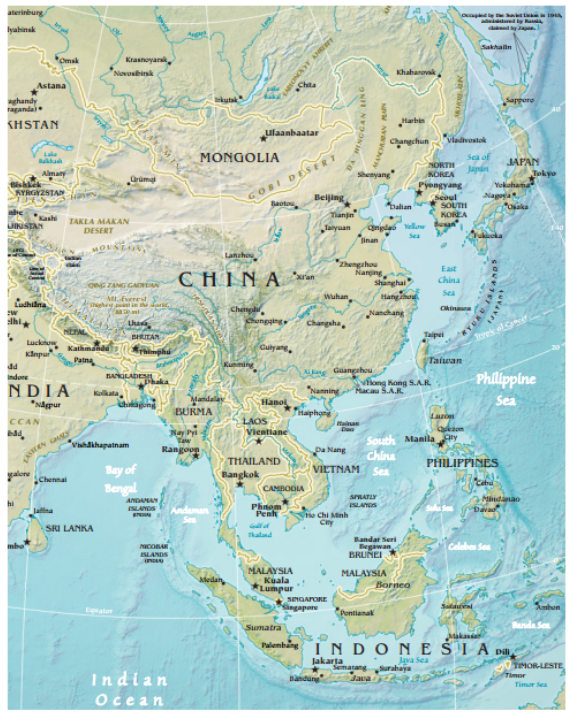
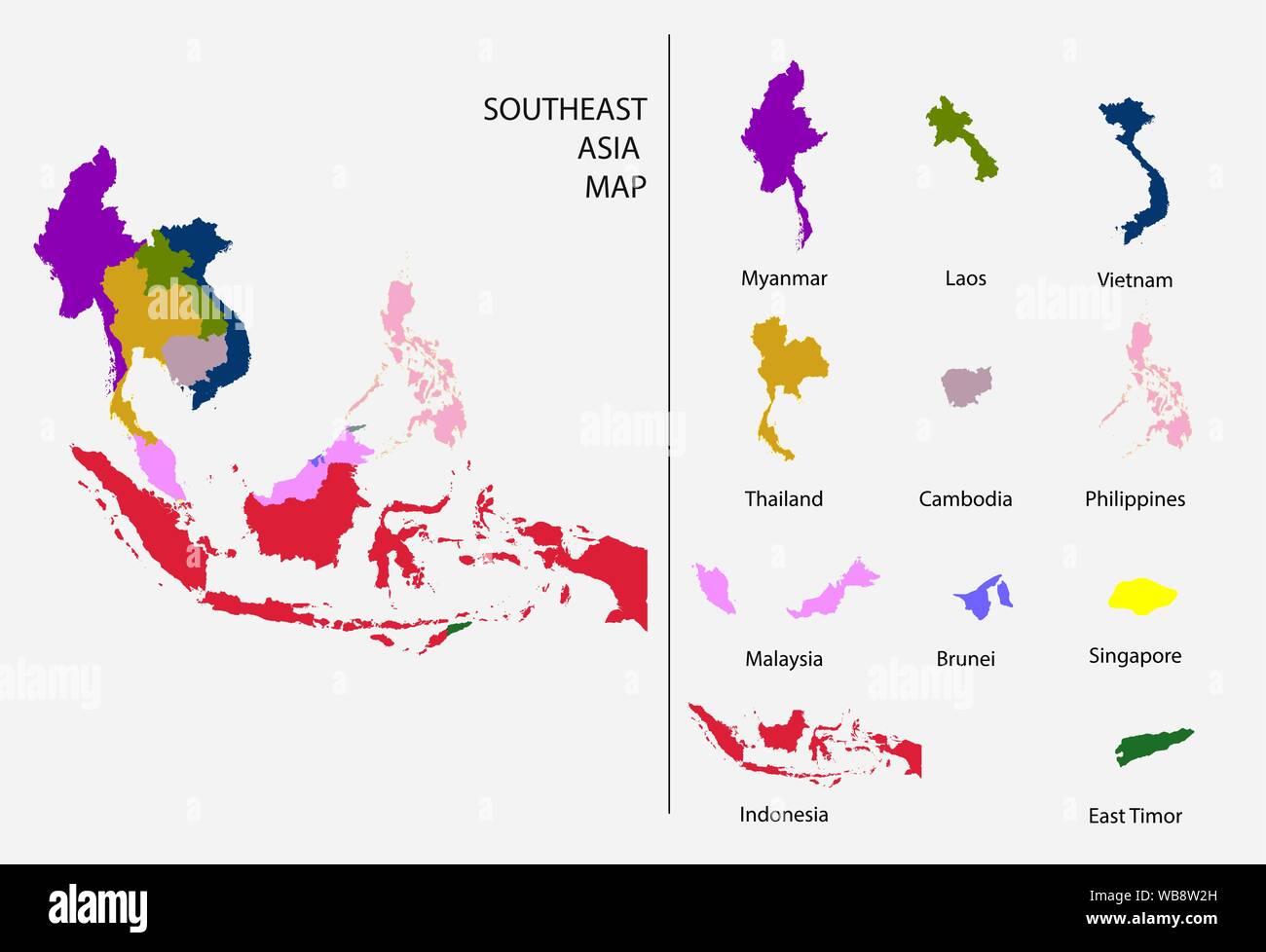
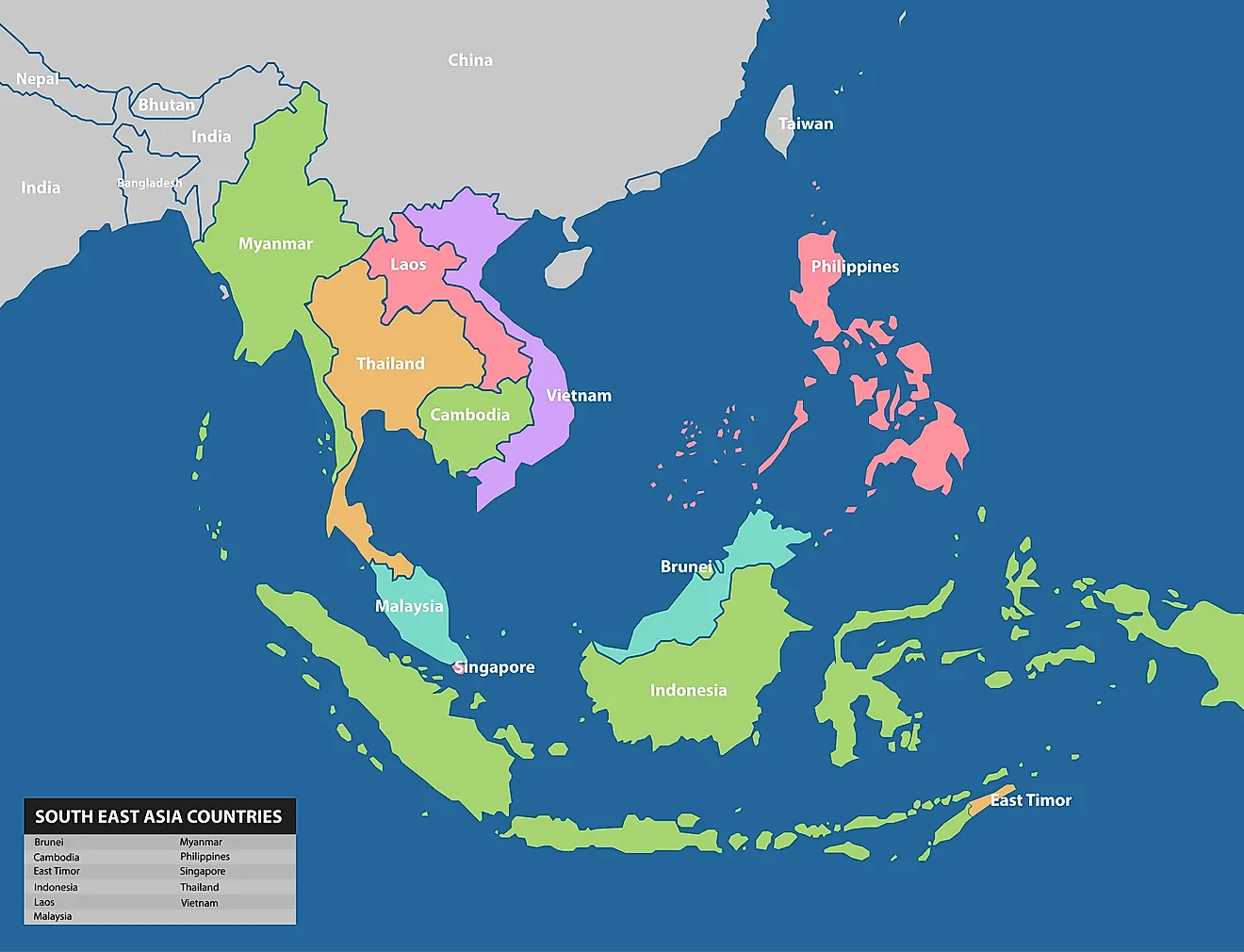
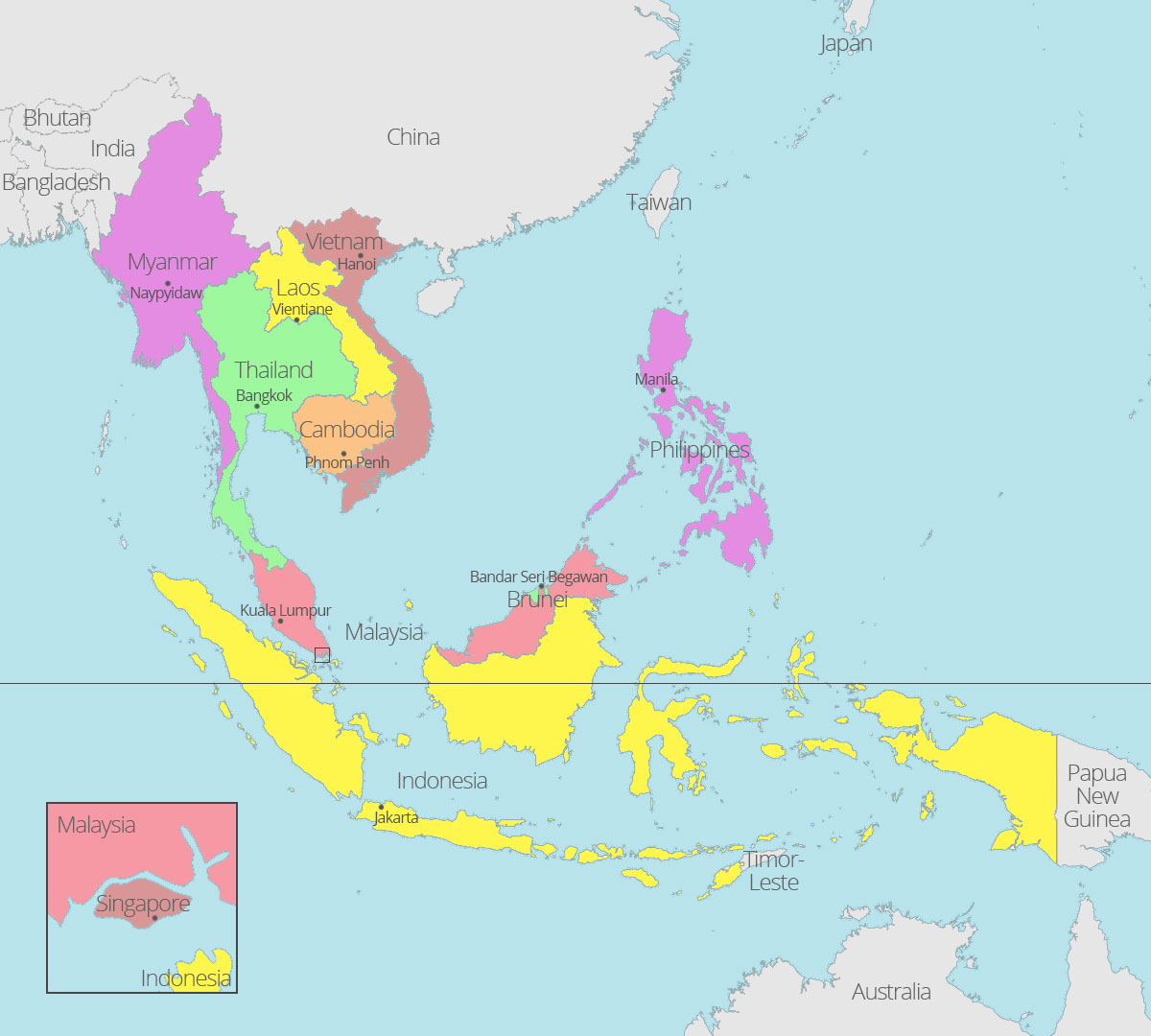
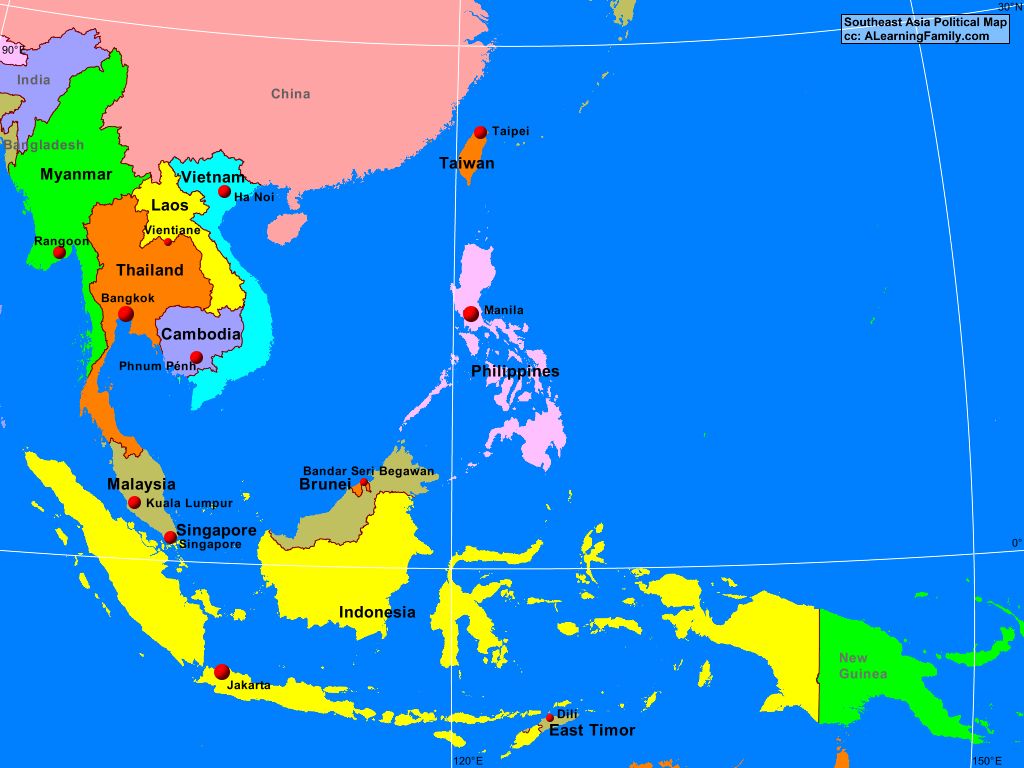
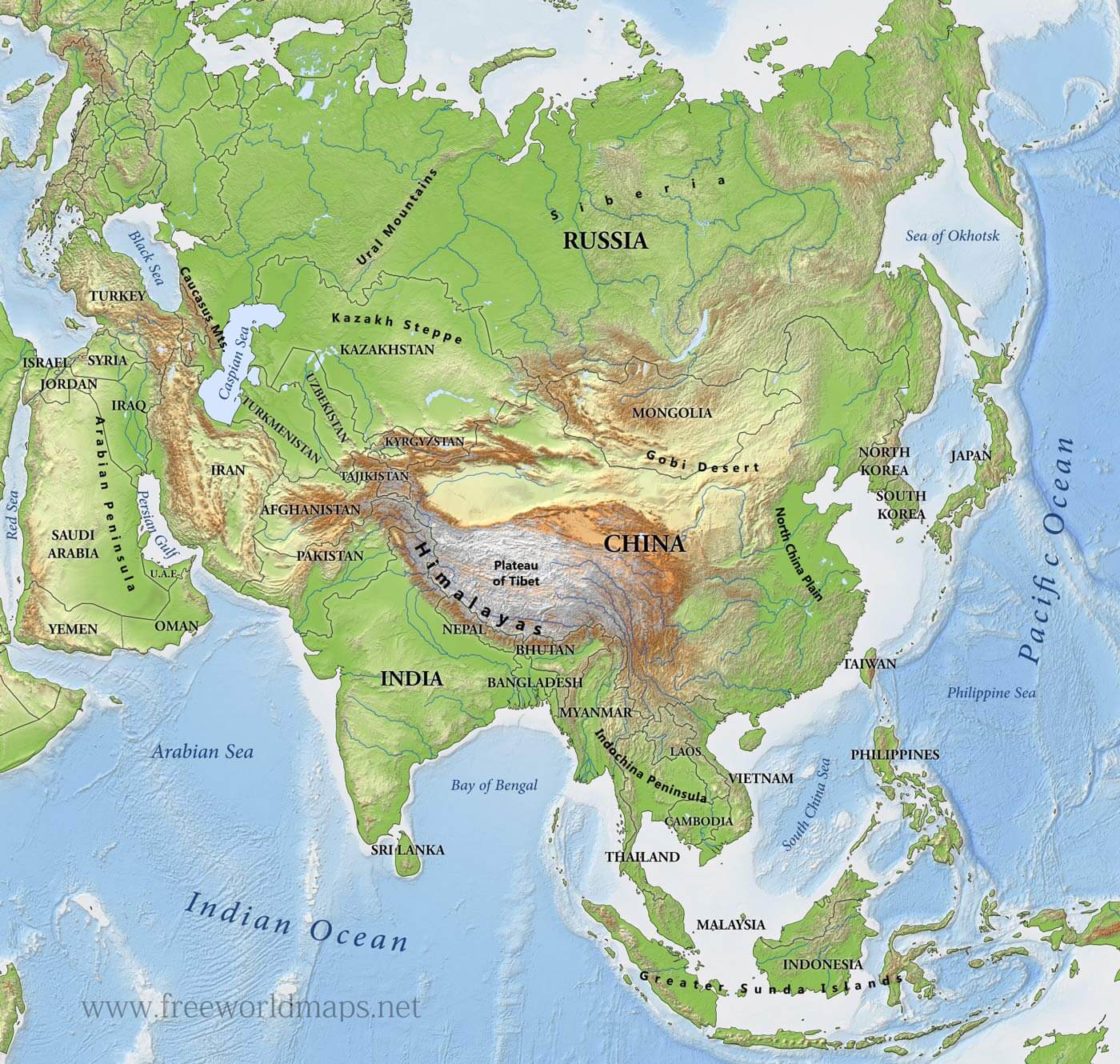
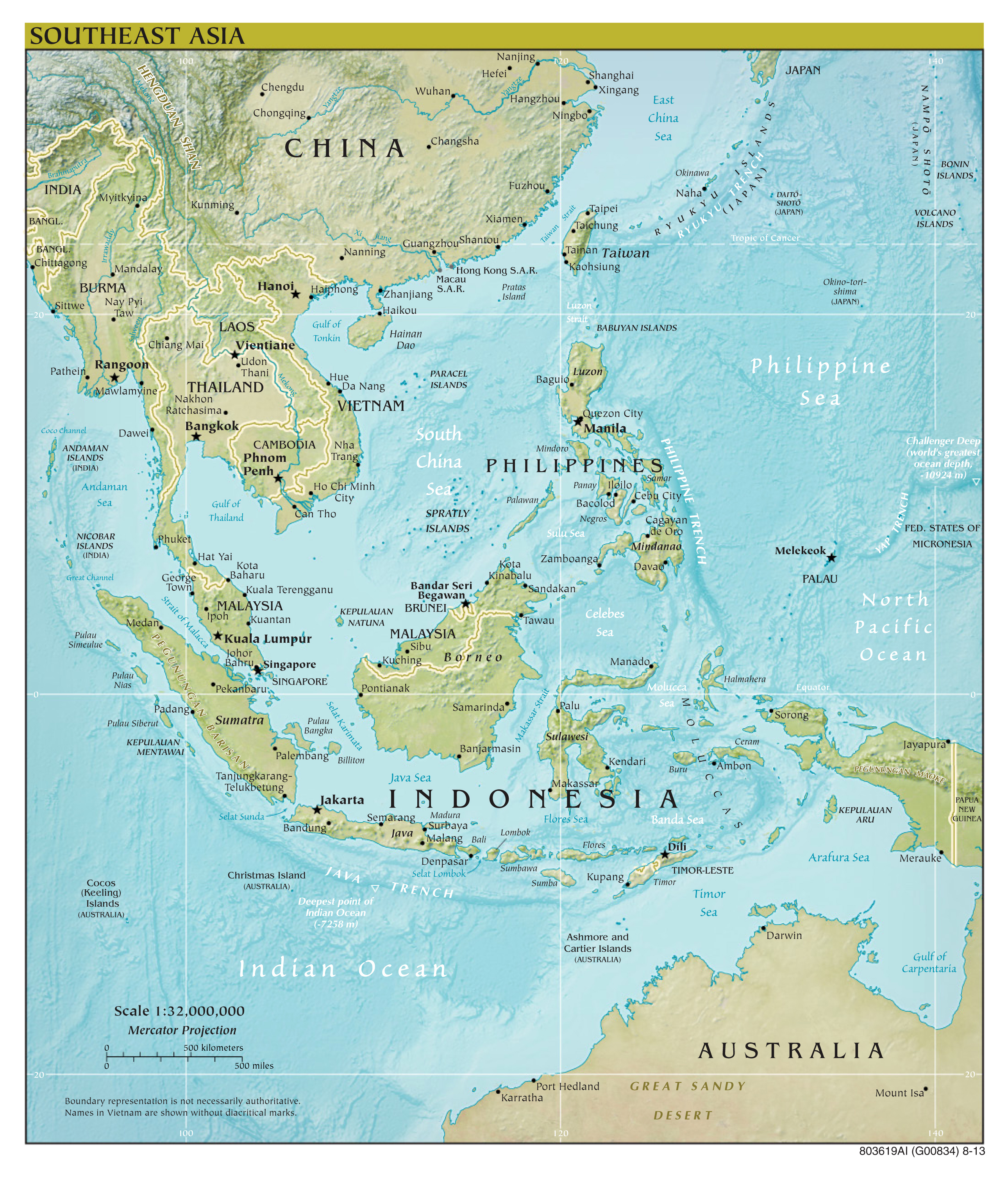
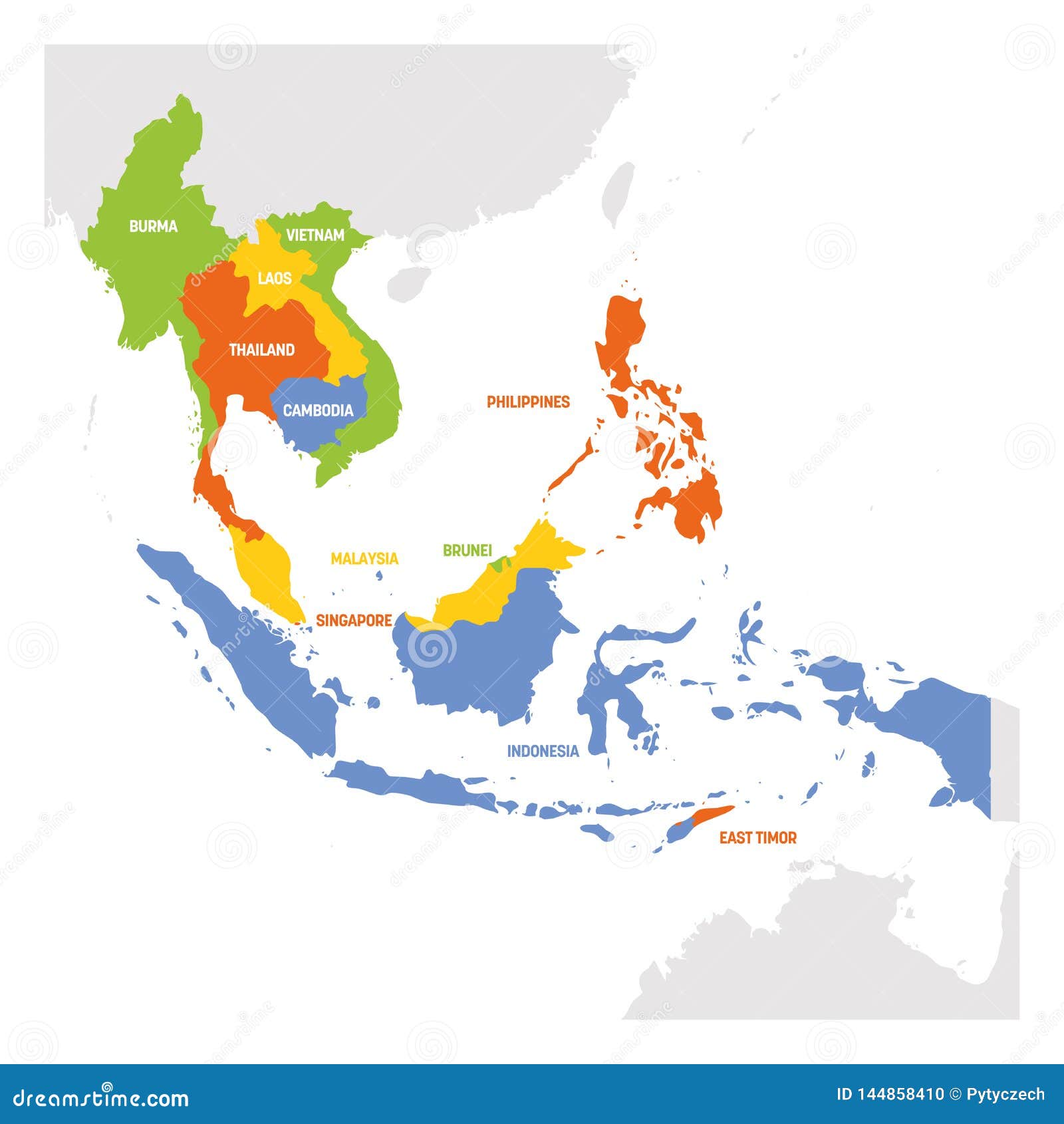
Southeast Asia is a subregion of Asia, comprising the countries geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. It includes two distinct parts: mainland Southeast Asia (also known as Indochina) and maritime Southeast Asia.
- Mainland Southeast Asia: Consists of Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam. This area is characterized by mountainous terrain interspersed with fertile river valleys, most notably the Mekong River.
- Maritime Southeast Asia: Comprises Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, the Philippines, Brunei, and East Timor. This area is an archipelago dominated by islands of varying sizes, shapes, and geological origins.
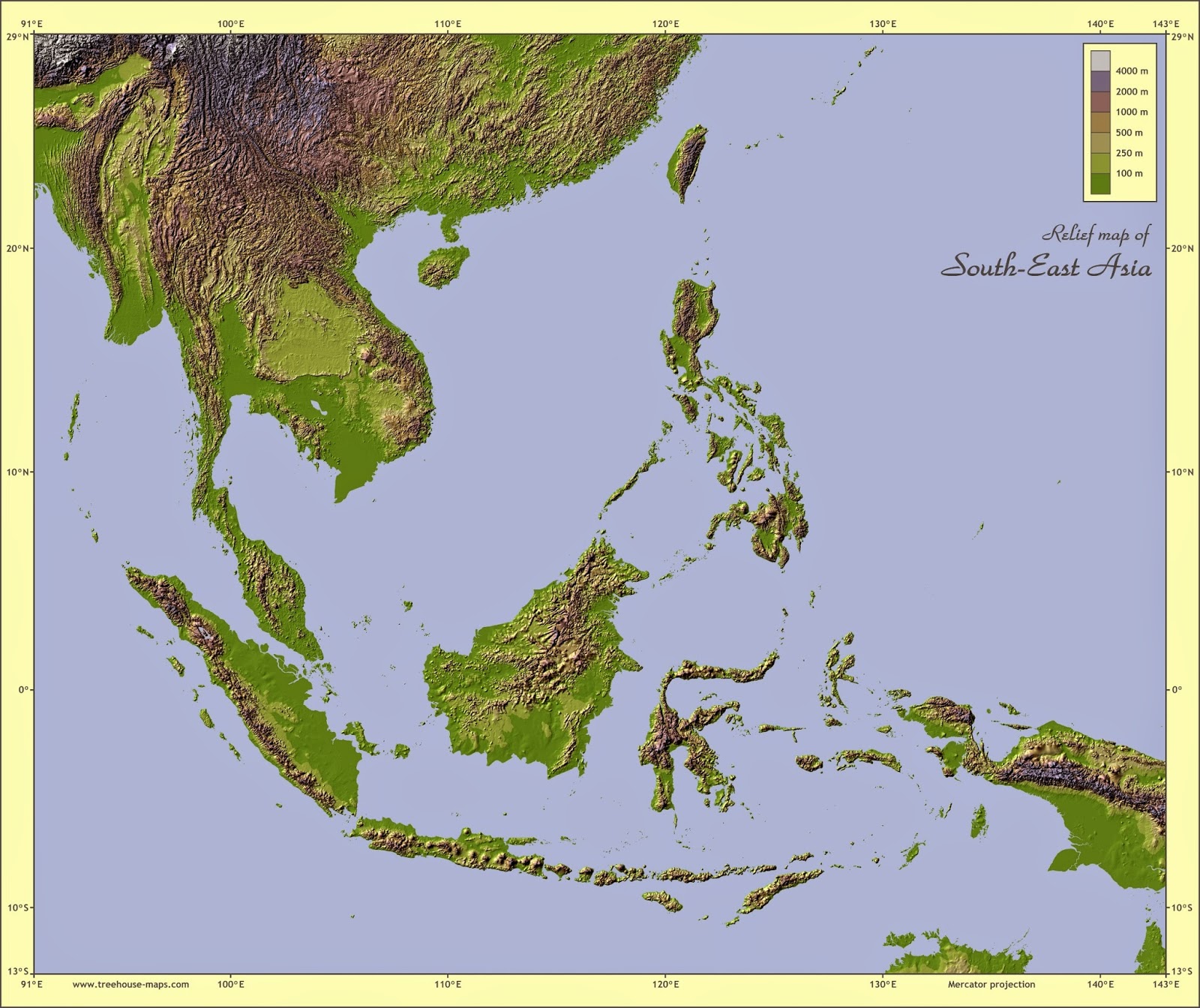
The region lies at the crossroads of major tectonic plates, leading to frequent seismic activity, including earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
2. The Shaping Forces: Tectonics and Southeast Asia Geography Map
The region's complex geography is largely a result of its location on the Eurasian, Indo-Australian, and Philippine Sea tectonic plates. This dynamic interaction has shaped the landscape in significant ways:
- Mountain Ranges: The collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates created the Himalayan mountain range, which extends southward into mainland Southeast Asia, forming mountain ranges like the Arakan Mountains in Myanmar and the Annamite Range in Vietnam.
- Volcanic Activity: The subduction of the Indo-Australian Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate has resulted in a volcanic arc extending through Indonesia and the Philippines, resulting in fertile volcanic soil and frequent eruptions. Mount Merapi in Indonesia is a prime example of an active volcano shaping the landscape and influencing local populations.
- Island Formation: Tectonic activity and volcanic eruptions have contributed to the formation of the numerous islands that comprise maritime Southeast Asia.
<img src="southeast_asia_tectonic_plates.jpg" alt="Southeast Asia Tectonic Plates Map" width="600" height="400">
<figcaption>A map illustrating the tectonic plates beneath Southeast Asia, showcasing their impact on the region's geology.</figcaption>3. Rivers and Waterways: The Lifelines of Southeast Asia Geography Map
Rivers are crucial to Southeast Asia's economy, culture, and ecosystems. They provide transportation, irrigation, and sustenance for millions of people.
- Mekong River: The longest river in Southeast Asia, flowing through six countries (China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam). It's vital for agriculture, fishing, and transportation.
- Irrawaddy River: Myanmar's most important river, used for transportation and irrigation. The river valley is a major agricultural region.
- Red River: Flows through northern Vietnam, creating a fertile delta used for rice cultivation.
- Salween River: Another major river flowing through Myanmar, Thailand, and China. It remains largely undammed, making it ecologically significant.
These waterways and the surrounding landscapes are accurately depicted and analysed through Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing technologies. GIS tools are increasingly trending this season due to advancements in geospatial data collection and analysis, which help in resource management and disaster preparedness.
4. Climatic Zones and Southeast Asia Geography Map
Southeast Asia experiences a predominantly tropical climate, influenced by monsoons and varying topography.
- Tropical Rainforest Climate: Characterized by high temperatures and rainfall throughout the year, found in areas like Malaysia, Indonesia, and parts of the Philippines. This climate supports lush rainforests teeming with biodiversity.
- Tropical Monsoon Climate: Defined by distinct wet and dry seasons, prevalent in mainland Southeast Asia and parts of the Philippines. The monsoon season brings heavy rainfall, essential for agriculture but also posing risks of flooding.
- Tropical Savanna Climate: Found in areas with a pronounced dry season, such as parts of Myanmar, Thailand, and Indonesia.
Variations in altitude also create diverse microclimates, supporting unique ecosystems.
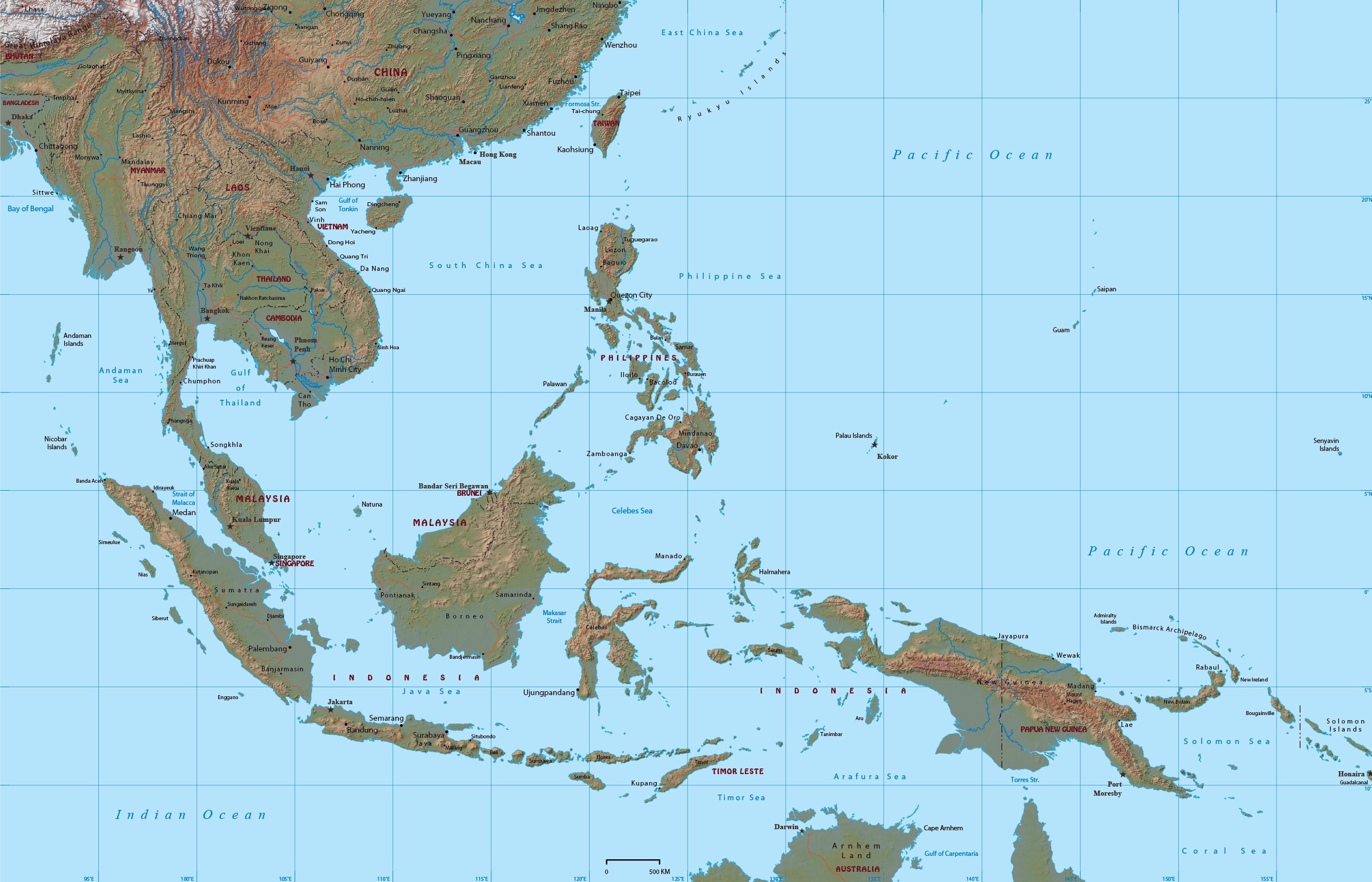
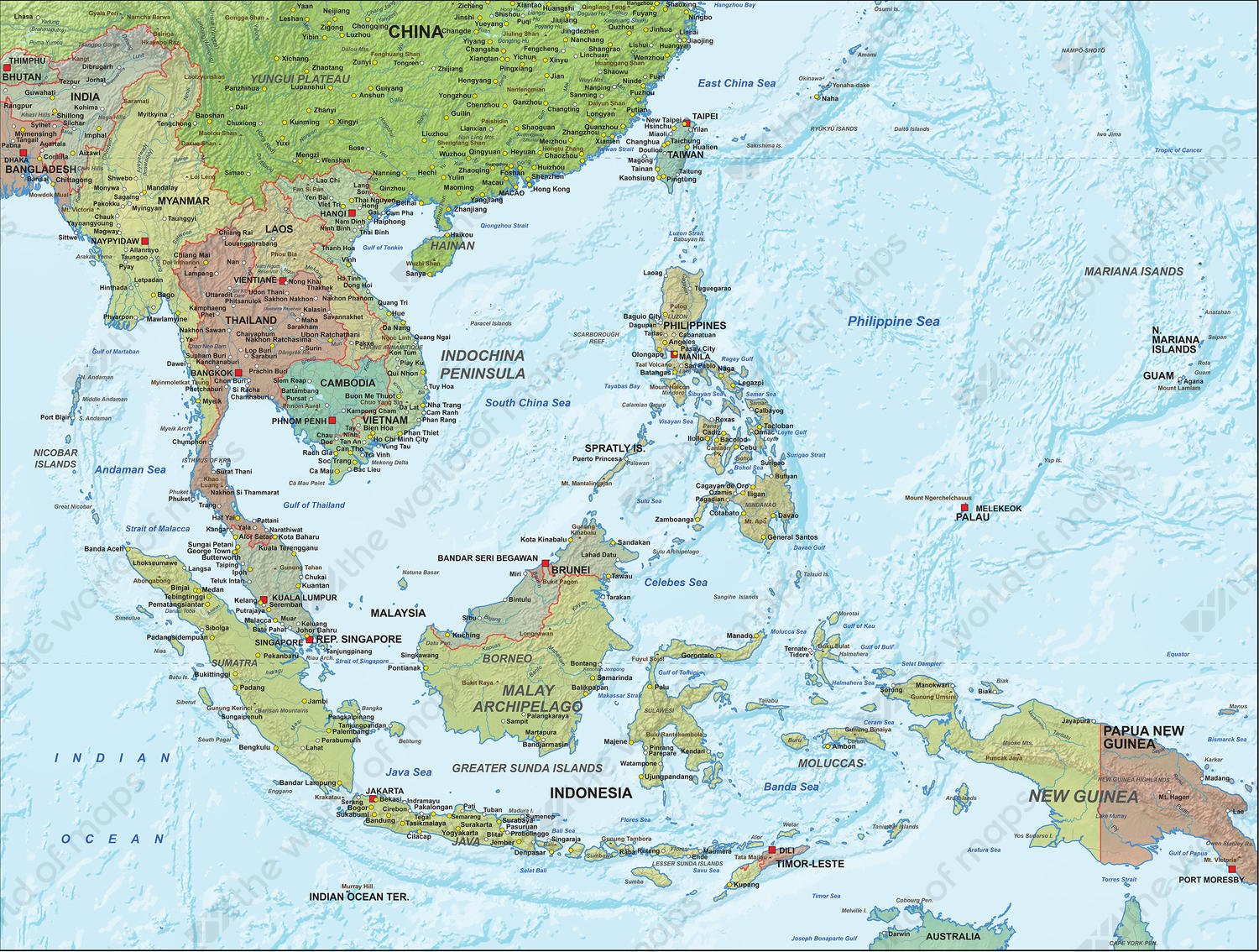
5. Coastlines and Seas: Defining Southeast Asia Geography Map
The extensive coastlines and seas of Southeast Asia play a vital role in the region's trade, fishing industry, and tourism.
- Strategic Waterways: The Strait of Malacca, the South China Sea, and the Java Sea are important shipping lanes connecting Asia with the rest of the world. Control over these waterways is strategically important.
- Coastal Ecosystems: Mangrove forests, coral reefs, and seagrass beds provide crucial habitats for marine life and protect coastlines from erosion. These ecosystems are under threat from pollution and overfishing.
- Island Nations: Countries like Indonesia and the Philippines are archipelagic nations, with thousands of islands that contribute to their rich cultural and biological diversity.
<img src="southeast_asia_coastline.jpg" alt="Southeast Asia Coastline Map" width="600" height="400">
<figcaption>An overview of Southeast Asia's coastline, highlighting key waterways and island formations.</figcaption>6. Natural Resources and Southeast Asia Geography Map
Southeast Asia is rich in natural resources, including:
- Oil and Gas: Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei, and Vietnam are major producers of oil and natural gas.
- Minerals: The region is abundant in tin, bauxite, copper, nickel, and other minerals. Indonesia and the Philippines are particularly rich in mineral resources.
- Timber: Tropical rainforests provide valuable timber resources, although sustainable forestry practices are crucial to prevent deforestation.
- Agricultural Resources: Rice, rubber, palm oil, coffee, and spices are important agricultural products.
7. Urbanization and Southeast Asia Geography Map
Southeast Asia is experiencing rapid urbanization, with major cities like Jakarta, Bangkok, Manila, and Ho Chi Minh City growing rapidly. This growth presents both opportunities and challenges:
- Economic Growth: Urban centers are hubs of economic activity, attracting investment and creating jobs.
- Infrastructure Development: Rapid urbanization requires significant investment in infrastructure, including transportation, housing, and sanitation.
- Environmental Challenges: Urban growth can lead to pollution, traffic congestion, and pressure on natural resources.
GIS and spatial planning are becoming increasingly important for managing urban growth and addressing environmental challenges. The trending topic of "smart cities" in Southeast Asia relies heavily on accurate geographic data and analysis.
8. Challenges and Opportunities: Climate Change and Southeast Asia Geography Map
Climate change poses significant challenges to Southeast Asia, including:
- Sea Level Rise: Coastal areas are vulnerable to sea level rise, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Extreme Weather Events: The region is experiencing more frequent and intense typhoons, floods, and droughts.
- Deforestation: Deforestation contributes to climate change and biodiversity loss.
However, there are also opportunities:
- Renewable Energy: Southeast Asia has significant potential for renewable energy development, including solar, wind, and hydropower.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Promoting sustainable agricultural practices can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect natural resources.
- Climate Adaptation: Implementing climate adaptation measures can help communities cope with the impacts of climate change.
This season, the trending focus on climate resilience and sustainable development is driving innovation in geospatial technologies, enabling better climate modeling and resource management.
Q: What are the two main parts of Southeast Asia? A: Mainland Southeast Asia and Maritime Southeast Asia.
Q: What are the major rivers in Southeast Asia? A: Mekong River, Irrawaddy River, Red River, Salween River.
Q: How does tectonic activity affect Southeast Asia's geography? A: It creates mountain ranges, volcanic activity, and contributes to island formation.
Q: What are some major challenges facing Southeast Asia due to climate change? A: Sea level rise, extreme weather events, and deforestation.
Q: How are GIS and spatial planning used in Southeast Asia? A: For managing urban growth, addressing environmental challenges, and climate modeling.
Keywords: Southeast Asia, Geography, Map, Mekong River, Tectonics, Climate Change, GIS, Natural Resources, Urbanization, Maritime Southeast Asia, Mainland Southeast Asia, Environment, Asia Geography, Trending, Seasonal.
Summary Question and Answer: Southeast Asia comprises mainland and maritime regions shaped by tectonics, its rivers are vital, climate is tropical, GIS aids planning, and climate change poses challenges.







5 Free Printable Southeast Asia Map Labeled With Countries PDF Download Southeast Asia Map Map Southeast Asia Hi Res Stock Photography And Images Alamy Southeast Asia Map Graphic Vector Separated Isolated Country Map For Design Work Or Info Graphic Education And Geography WB8W2H Political Map Of Asia Nations Online Project Asia Map Map Of Southeast Asia With Countries Stawl Large Map Of Asia Southeast Asia Region Map Countries Southeastern Asia Vector Illustration Southeast Asia Region Map Countries 144858410 Asia Physical Map Freeworldmaps Net Asia Physical Map
Deciphering Southeast Asia A Geographical And Political Overview AsiaSEPolitical Political Map Of Southeast Asia Southeast Asia Asia Mapsland Political Map Of Southeast Asia Small Southeast Asia Physical Map Southeastasia Peaks Map Southeast Asia Physical Map Southeastasia Physical Map South Asia Physical Map Southasia Physical Map Asia Political Map 2022 ASEAN Map
Karta Sydostasien Southeast Asia Australia Europa Karta Clipboard Eadfdc7fa9e5d3e3892e2c1198e32c360 Physical Map Of Asia Ezilon Maps Asia Physical Map Printable Map Of Southeast Asia Southeast Asia Map Countries Lovely Digital Political Map South East Asia With Relief 1313 South Asia Map Physical 8284a2f26cf73d5b1d35b585e44d461a
Physical Maps Of Southeast Asia Relief Map Se Asia Physical Maps Of Southeast Asia Se Asia Relief Map Topographic Large Detailed Political Map Of South Asia With Major Cities 1998 Large Detailed Political Map Of South Asia With Major Cities 1998 Chapter 11 Southeast Asia World Regional Geography 30cc59acc5d823dc293e4f23b8061303 Map Of Southeast Asia Infographics Google Slides PPT 1 Map Of Southeast Asia Infographics Media Library Original 1600 900 What Are The Two Main Branches Of Geography WorldAtlas Southeast Asian Countries Printable Map Of Southeast Asia Large Scale Political Map Of Southeast Asia With Relief Capitals And Major Cities 2013 Southeast Asia Physical Map Southeastasia Hd Map
Kort Southeast Political Asia Map Bykort Og Verdenskort Plakater P 137392 Recent Nasa Southeast Asia Hd 32322425116 2e743926e2 B

