Last update images today US Poverty Map: Understanding The Landscape
US Poverty Map: Understanding the Landscape
Poverty in the United States remains a complex and persistent challenge, affecting millions across the nation. Understanding its geographical distribution is crucial for effective policy-making and targeted interventions. This article delves into the "map of us poverty," exploring the key factors that contribute to its uneven spread and highlighting the areas most impacted.
Map of US Poverty: Introduction
The United States, despite being one of the wealthiest nations in the world, grapples with significant poverty rates. To effectively combat this issue, it's essential to analyze the geographical distribution of poverty across the country. A "map of us poverty" provides a visual representation of this distribution, revealing regional disparities and highlighting areas requiring focused attention. This article aims to break down this complex issue, offering insights into its causes, consequences, and potential solutions.
Target Audience: Policymakers, social workers, educators, community leaders, researchers, and anyone interested in understanding and addressing poverty in the United States.
Map of US Poverty: Defining and Measuring Poverty
Before exploring the "map of us poverty," it's important to understand how poverty is defined and measured. The official poverty measure (OPM), established by the U.S. government, considers a family's pre-tax income against a poverty threshold that varies based on family size and composition. However, the OPM has limitations.
-
Limitations of OPM:
- Does not account for regional variations in cost of living.
- Excludes non-cash benefits (e.g., SNAP, housing assistance).
- Fails to capture expenses like childcare and healthcare.
[Image of a family struggling to make ends meet, ALT text: "Family facing economic hardship, illustrating the realities of poverty in America."] Caption: The official poverty measure doesn't always paint the full picture of the struggles faced by low-income families.
The Supplemental Poverty Measure (SPM), introduced by the Census Bureau, addresses some of these limitations by considering factors such as housing costs, medical expenses, and government assistance programs. While SPM provides a more comprehensive picture, both measures are valuable tools for understanding the "map of us poverty."
Map of US Poverty: Regional Disparities in Poverty Rates
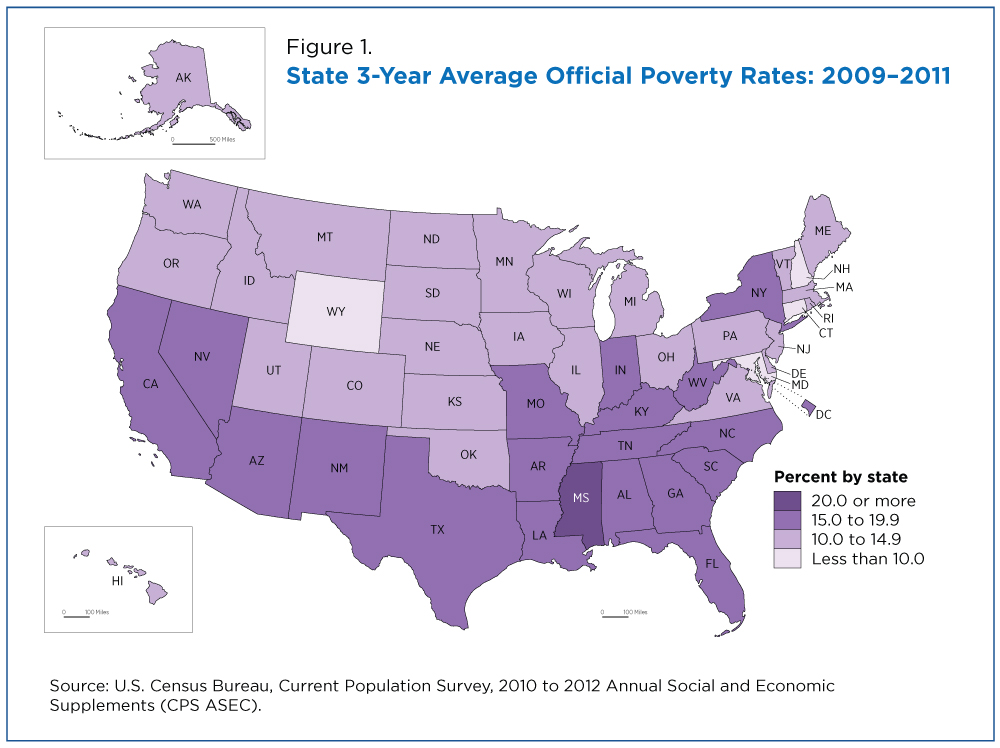
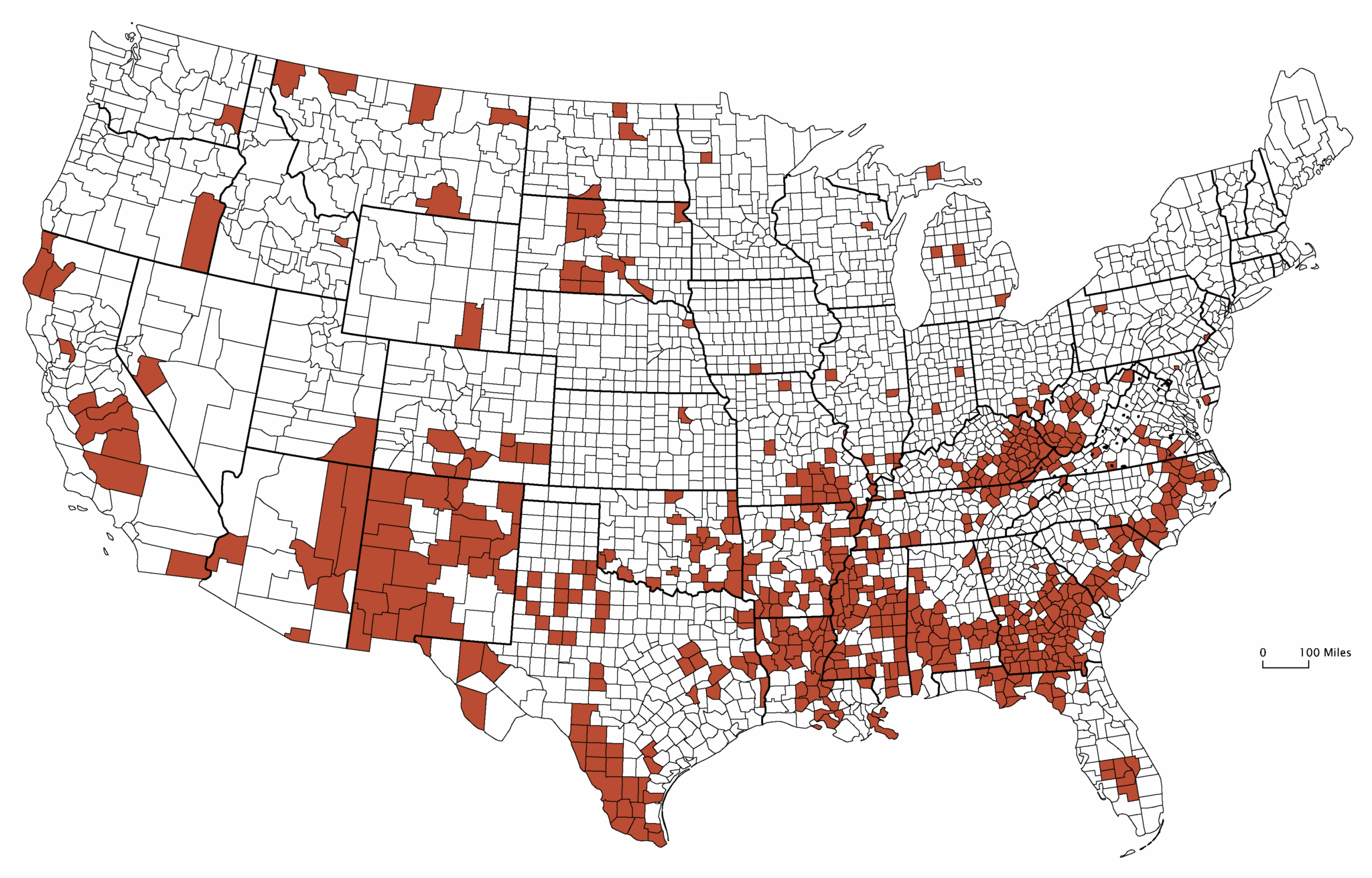
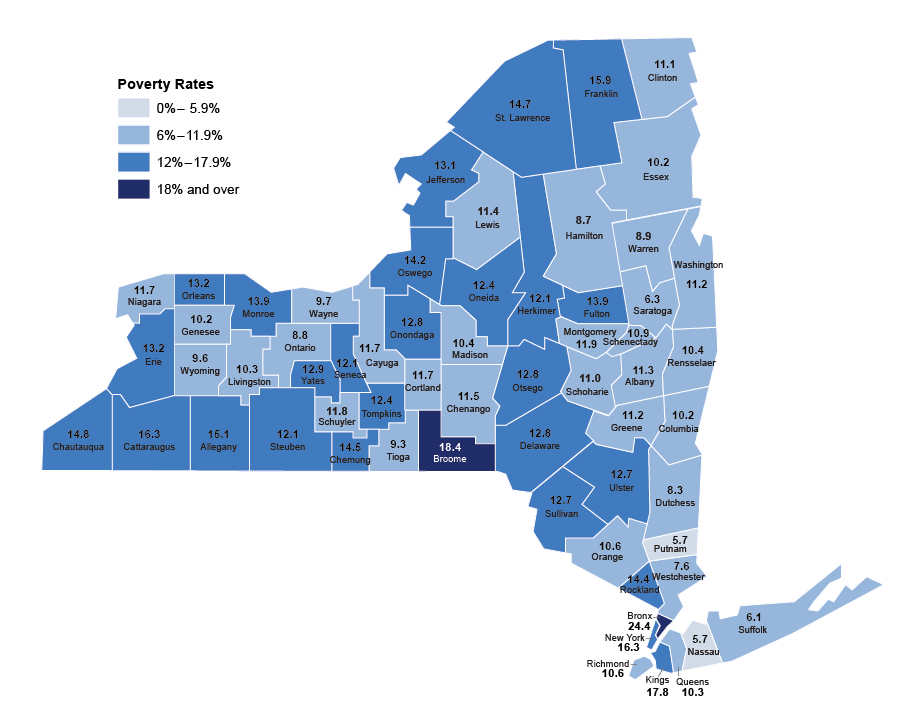
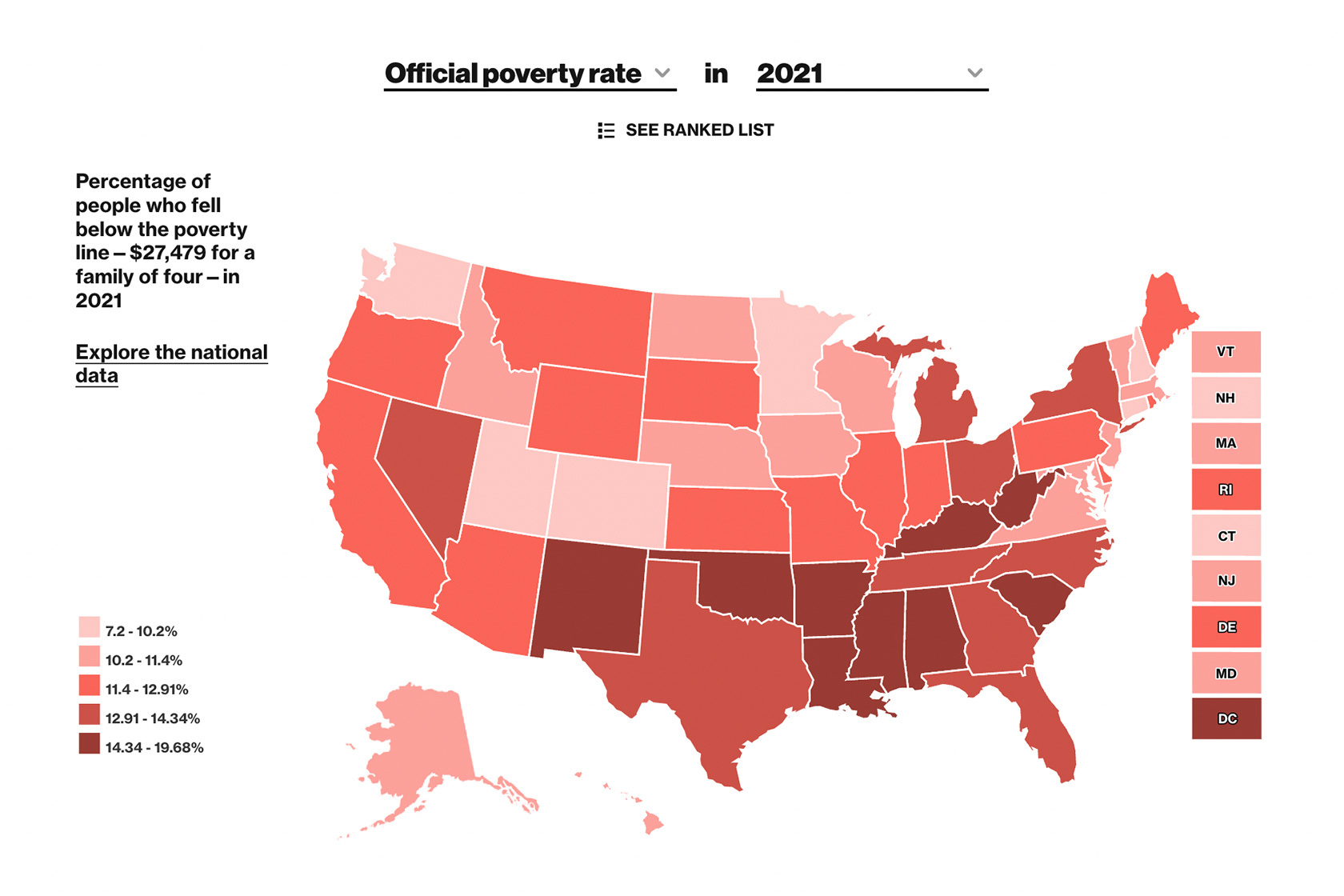
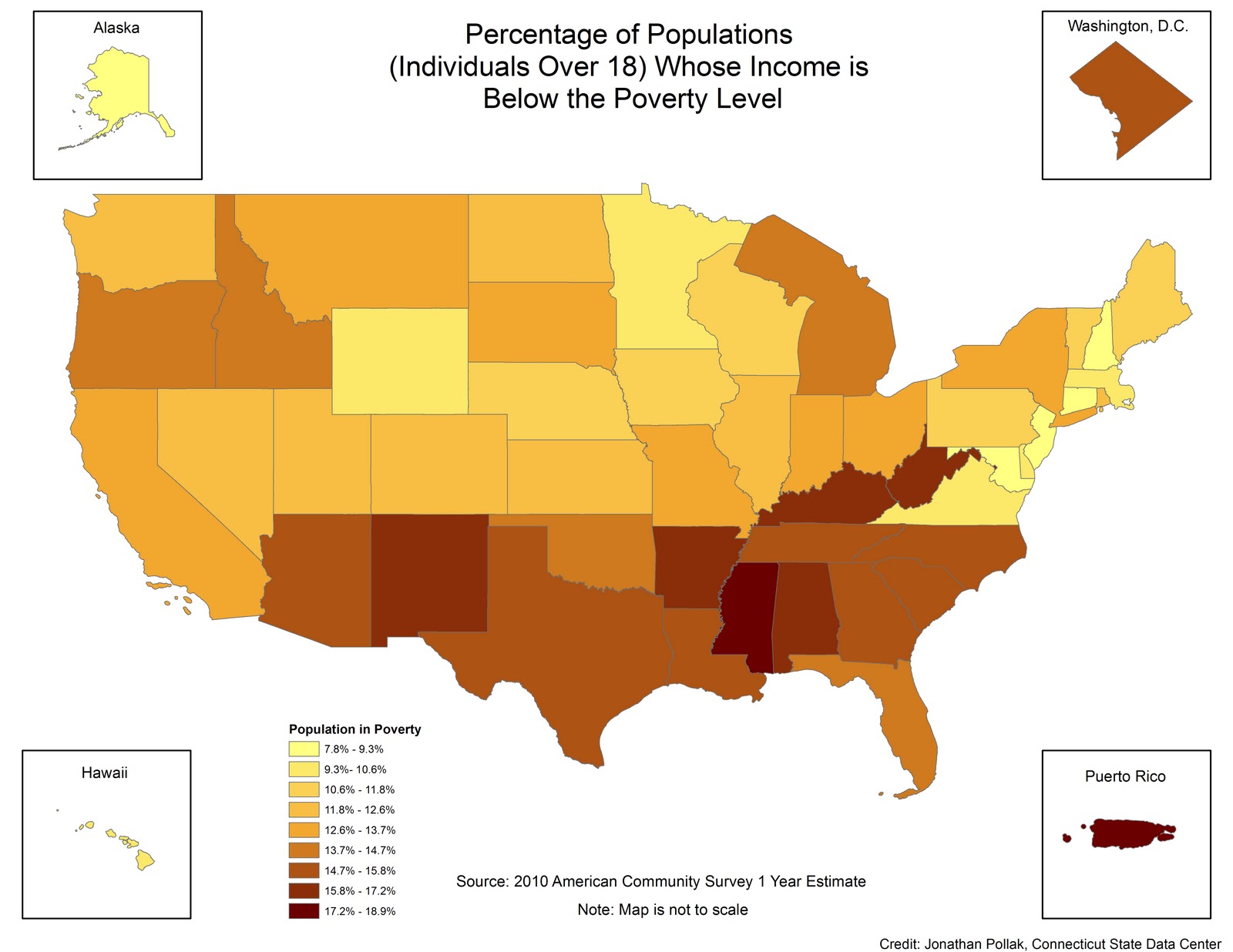
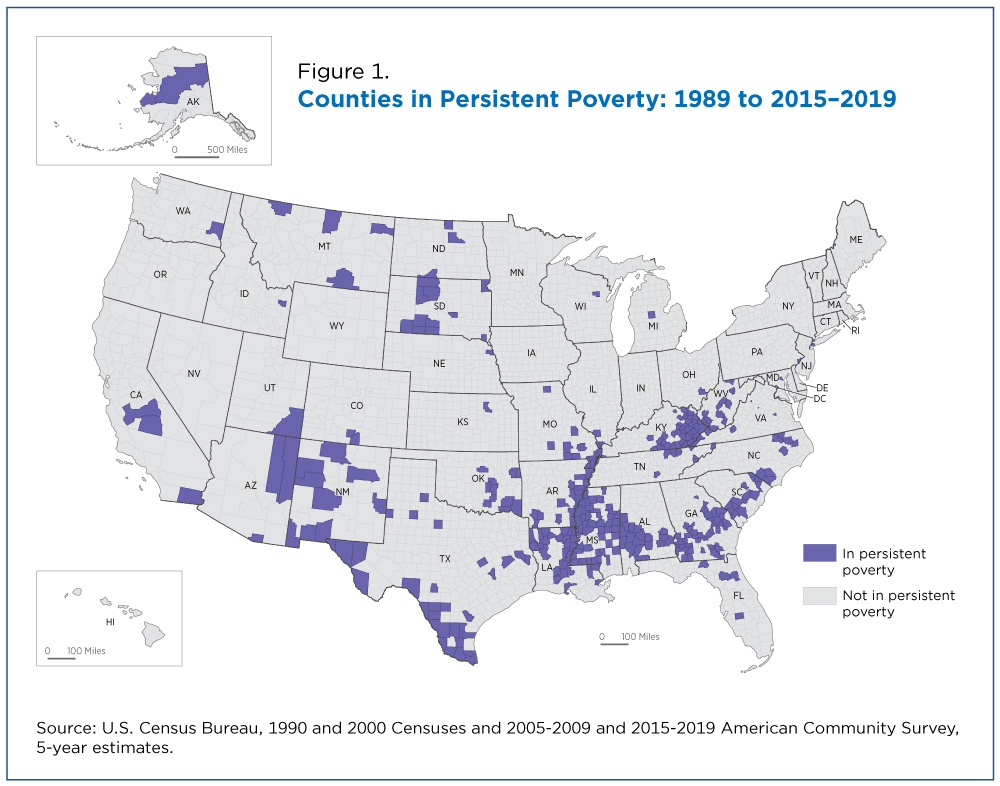
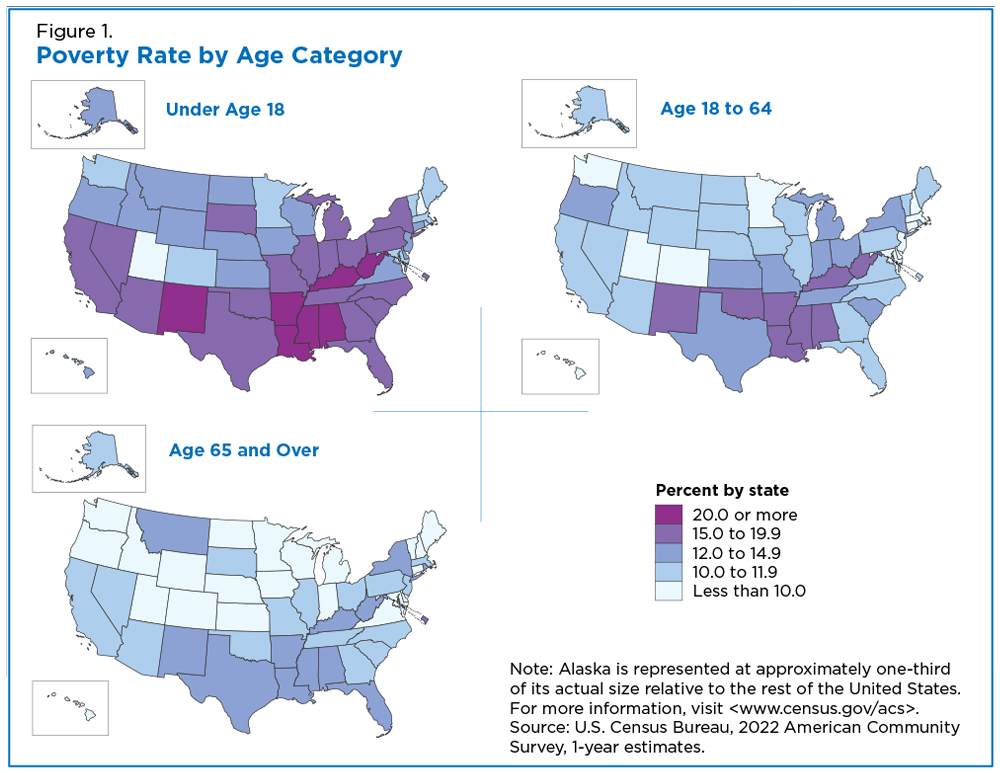
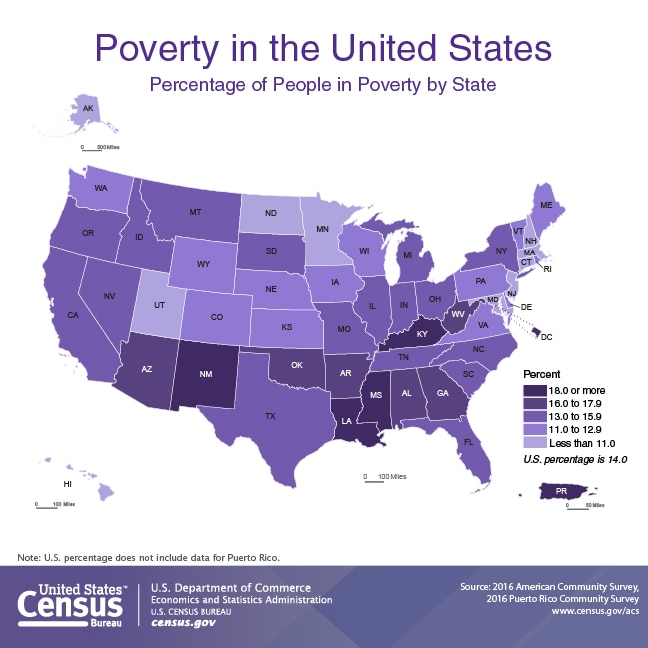
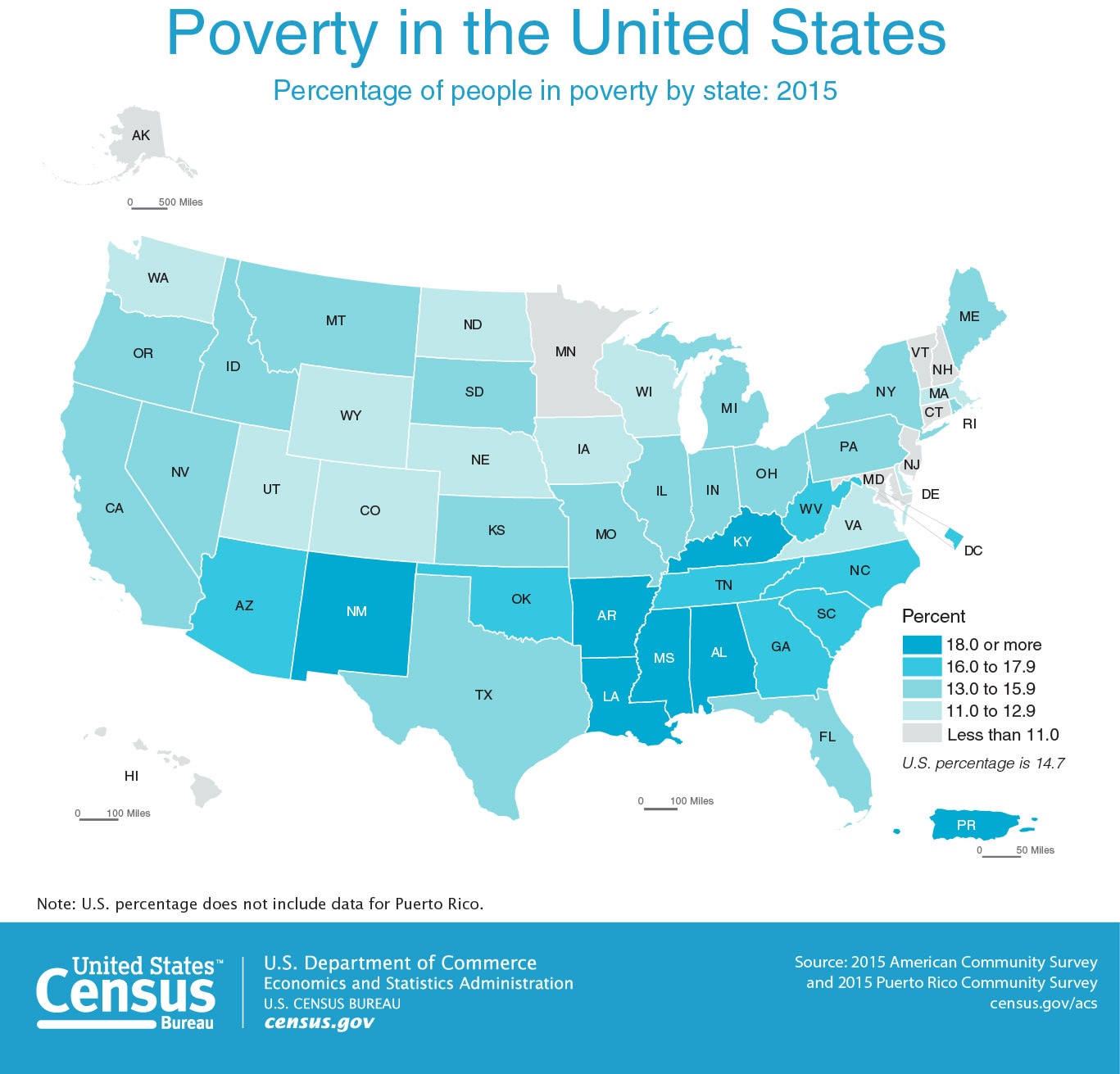
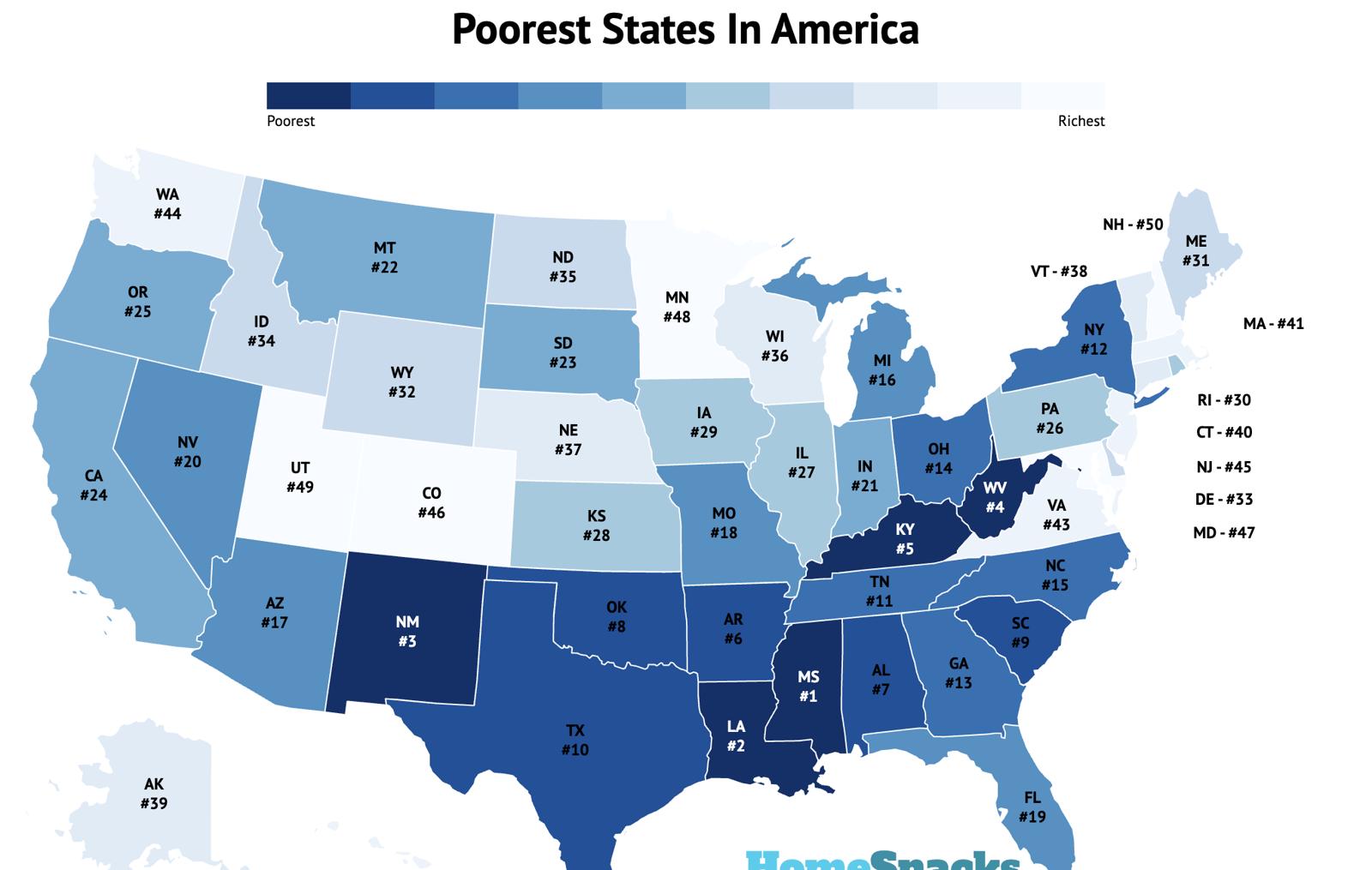
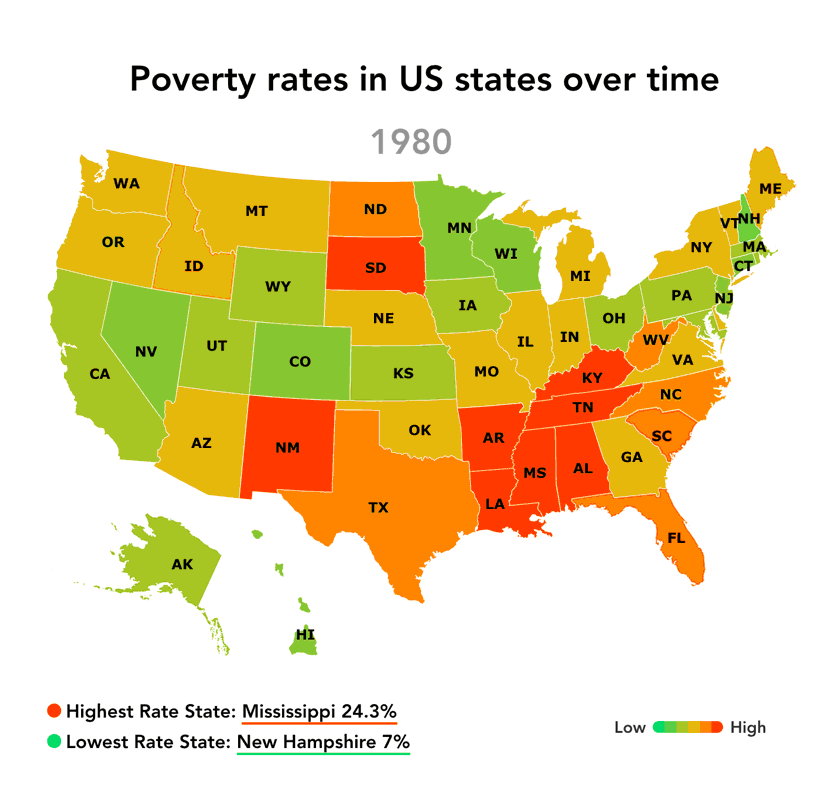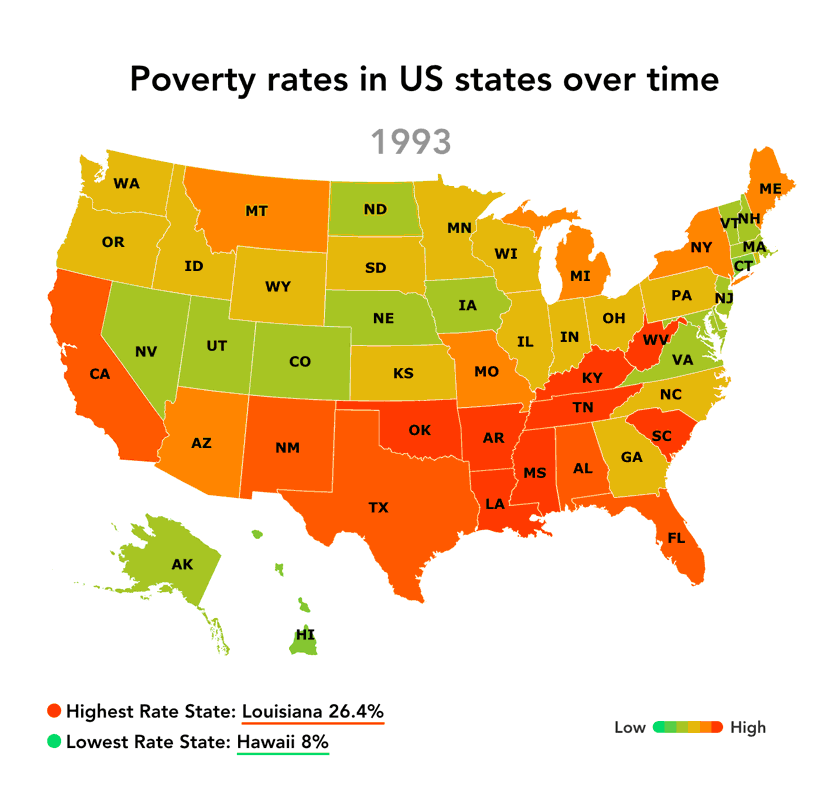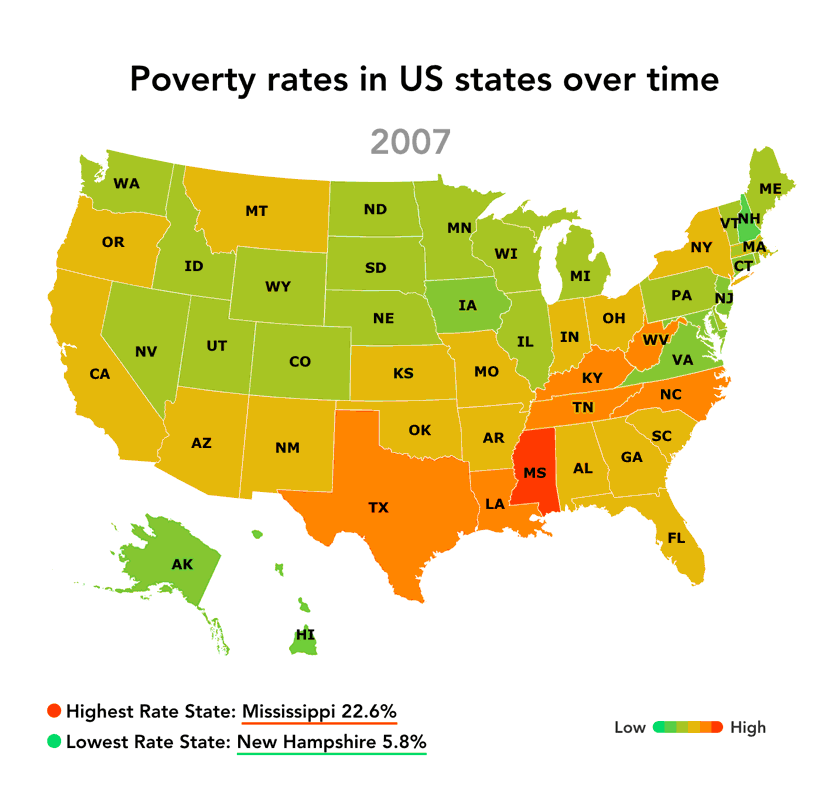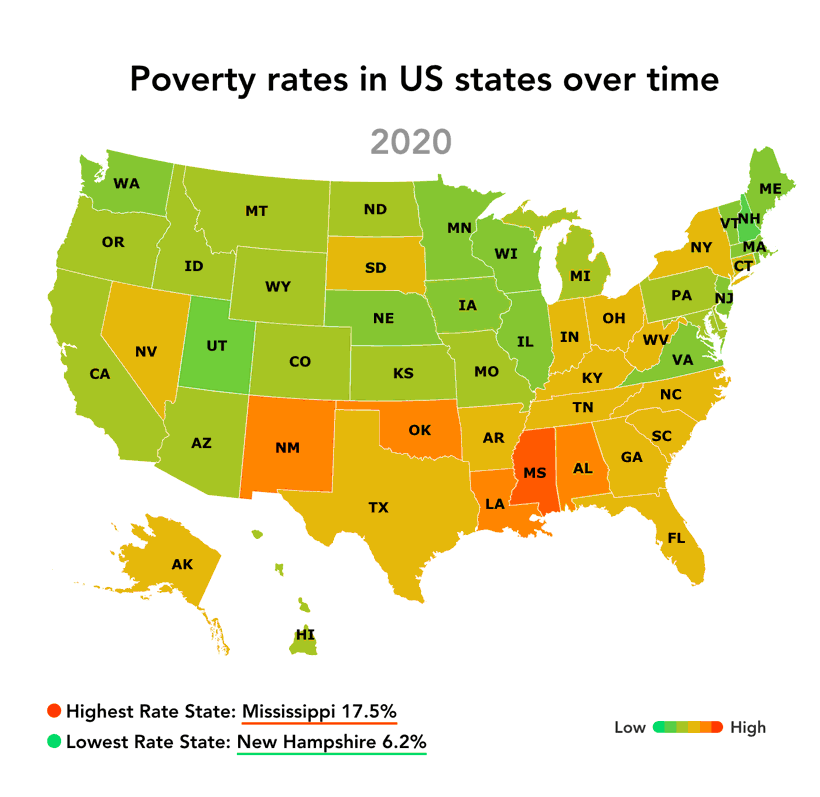
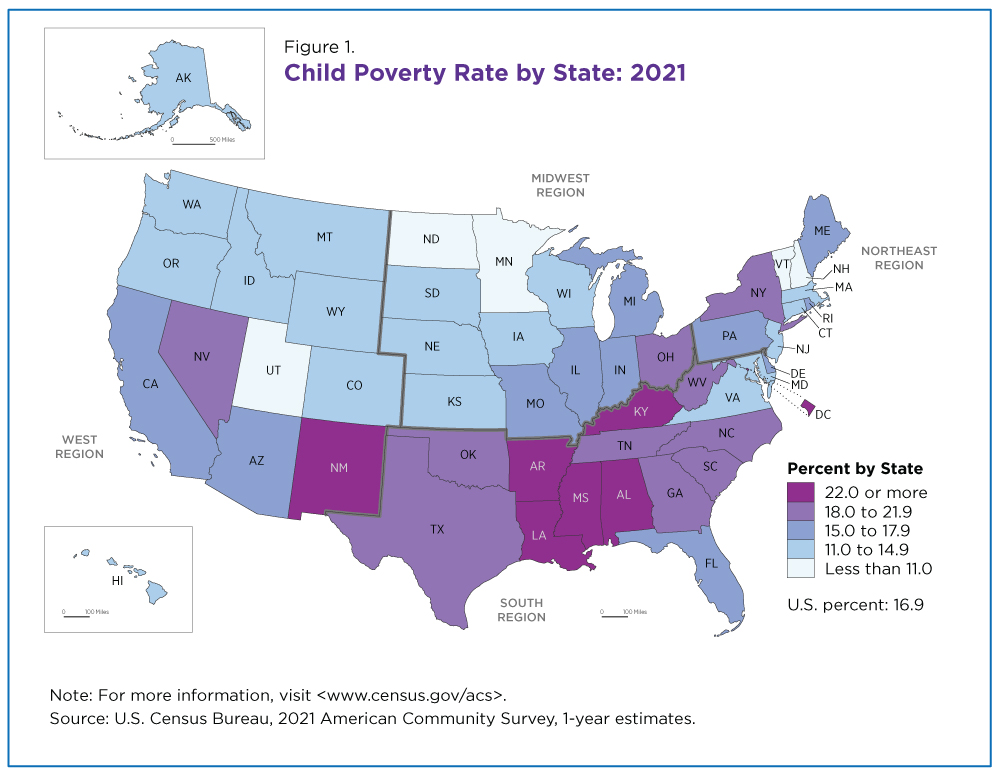
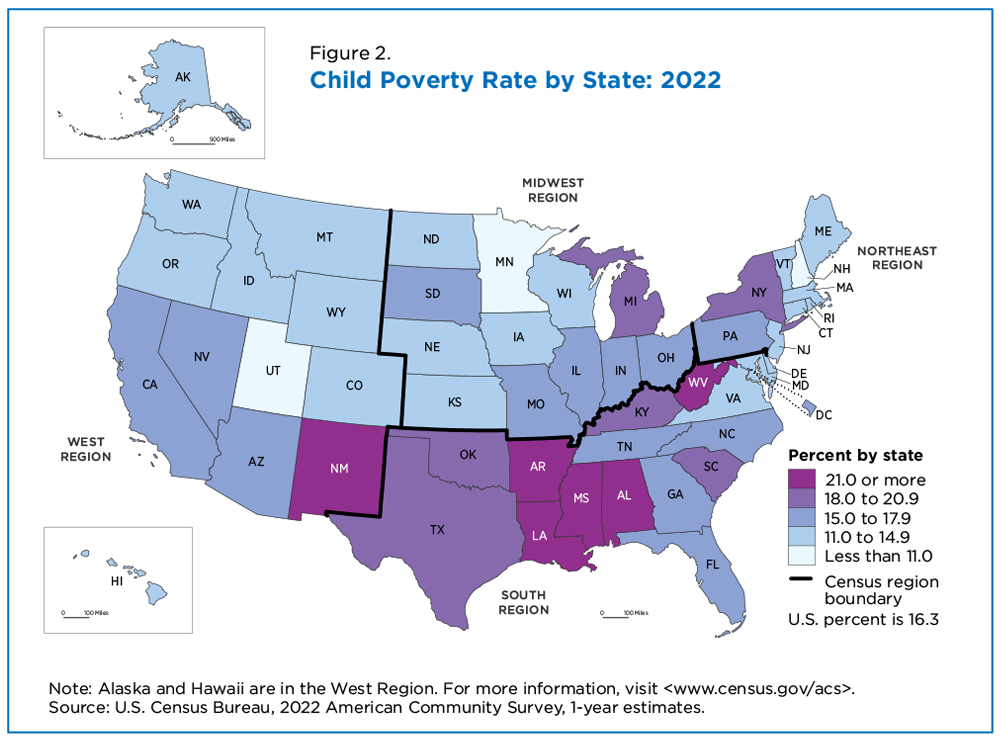
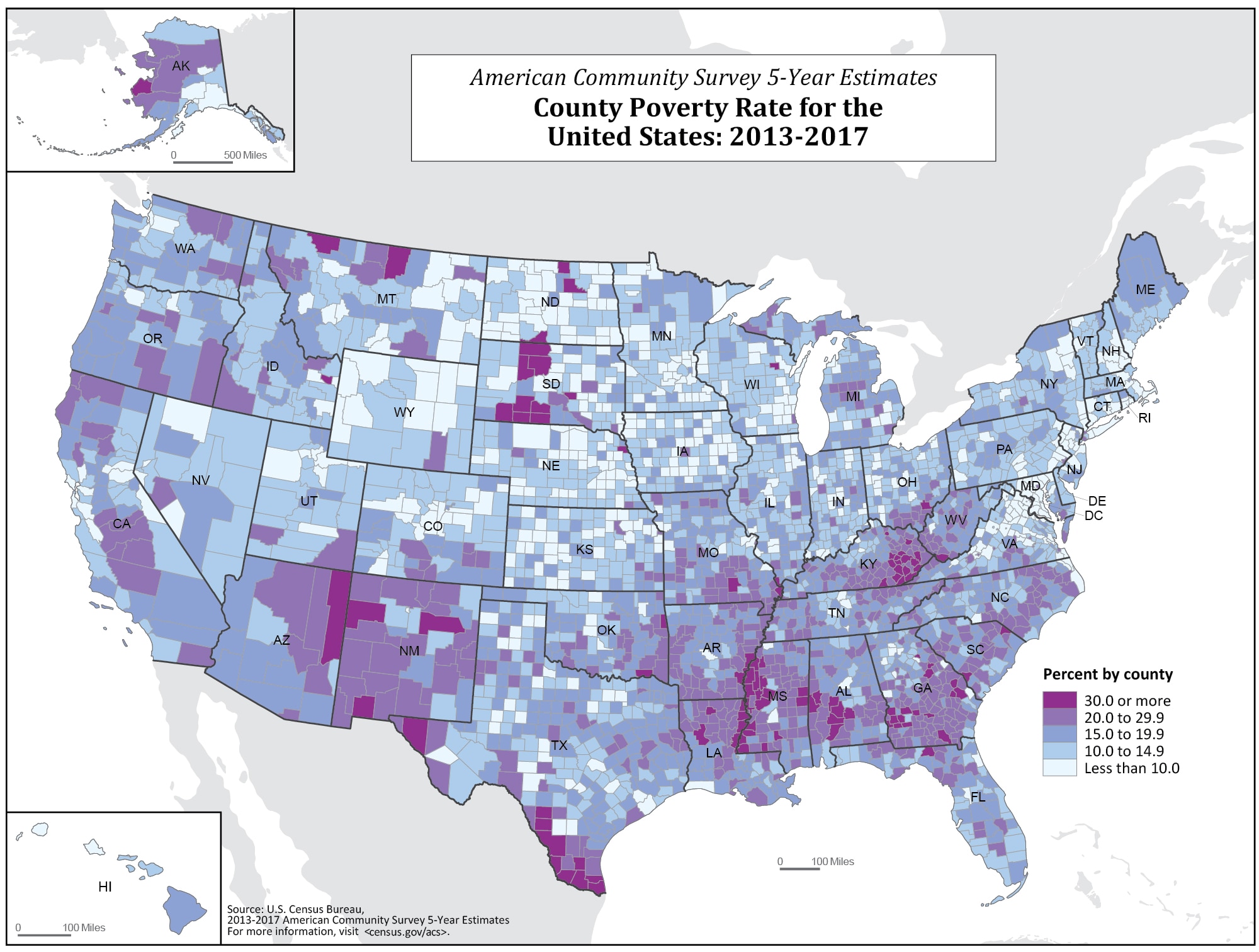
The "map of us poverty" reveals significant regional variations in poverty rates. The South consistently exhibits the highest poverty rates, followed by the West, Midwest, and Northeast.
-
The South: Factors such as historical legacies of slavery and discrimination, lower educational attainment, and limited economic opportunities contribute to high poverty rates in states like Mississippi, Louisiana, and Alabama.
-
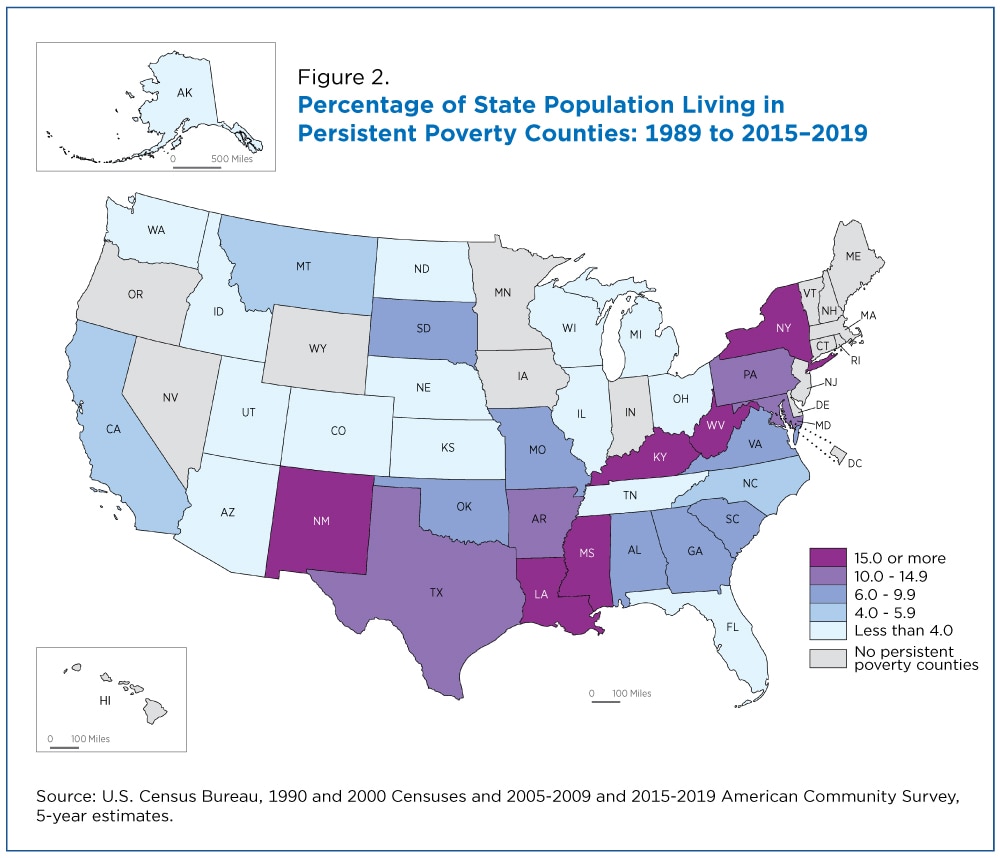
Rural Areas: Poverty is often concentrated in rural areas across the country, characterized by limited job opportunities, inadequate infrastructure, and a lack of access to essential services.
-
Urban Centers: While cities offer more opportunities, they also grapple with high poverty rates in specific neighborhoods, often due to factors like segregation, lack of affordable housing, and limited access to quality education and employment.
[Image of a map highlighting poverty rates by state, ALT text: "US Poverty Map showing regional disparities in poverty rates."] Caption: Poverty rates vary significantly across the United States, with the South and rural areas experiencing the highest rates.
Map of US Poverty: Key Factors Contributing to Poverty
Several interconnected factors contribute to the distribution reflected in the "map of us poverty."
- Education: Lack of access to quality education limits employment opportunities and earning potential.
- Employment: Unemployment, low-wage jobs, and lack of benefits perpetuate poverty.
- Healthcare: High healthcare costs and lack of access to affordable insurance can push families into poverty.
- Housing: The scarcity of affordable housing forces families to spend a large portion of their income on rent or mortgages, leaving less for other essential needs.
- Discrimination: Systemic discrimination based on race, ethnicity, and gender limits opportunities and contributes to poverty.
- Geography: Location limits access to job opportunities and quality services. [Image of children in underfunded school. ALT text: Underfunded schools limit economic opportunity for children. Caption: Investing in Education is vital to eradicating poverty.]
Map of US Poverty: Impact of Poverty on Communities
The high poverty rates reflected in the "map of us poverty" have far-reaching consequences for individuals and communities.
-
Health Outcomes: Poverty is linked to poorer health outcomes, including higher rates of chronic diseases, infant mortality, and mental health issues.
-
Educational Attainment: Children living in poverty are more likely to experience academic difficulties, drop out of school, and have limited opportunities for higher education.
-
Crime Rates: High poverty rates are associated with higher crime rates, creating unsafe communities and perpetuating cycles of poverty.
-
Social Mobility: Poverty limits social mobility, making it difficult for individuals and families to improve their economic circumstances.
[Image showing community outreach. ALT text: Community outreach provides assistance and opportunities to those struggling with poverty. Caption: Social program and community aid can help improve living standards.]
Map of US Poverty: Addressing Poverty - Potential Solutions
Combating poverty requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses the root causes and provides support to those in need.
-
Invest in Education: Increase funding for schools in low-income communities, provide access to early childhood education, and promote higher education opportunities.
-
Create Job Opportunities: Encourage businesses to locate in underserved areas, provide job training programs, and raise the minimum wage.
-
Expand Access to Healthcare: Ensure access to affordable healthcare through Medicaid expansion and other programs.
-
Increase Affordable Housing: Invest in affordable housing development, provide rental assistance, and combat housing discrimination.
-
Address Systemic Discrimination: Implement policies to combat discrimination based on race, ethnicity, and gender in education, employment, and housing.
-
Strengthen Social Safety Net: Expand programs like SNAP, TANF, and the Earned Income Tax Credit to provide a safety net for families in need.
-
Address Geographic Disadvantage: Invest in infrastructure in rural and underserved regions.
[Image of community gardens. ALT text: Community gardens provide fresh food in low income areas. Caption: Community led initiatives can also contribute to poverty eradication.]
Map of US Poverty: The Role of Technology
Technology can also play a significant role in addressing poverty.
- Digital Literacy: Providing digital literacy training and access to affordable internet can help individuals access online resources, find jobs, and improve their education.
- Telehealth: Telehealth can expand access to healthcare in rural and underserved areas.
- Online Education: Online education platforms can provide access to educational opportunities for individuals who cannot attend traditional schools or universities.
Map of US Poverty: Conclusion
The "map of us poverty" paints a stark picture of the uneven distribution of poverty in the United States. By understanding the factors contributing to this distribution and implementing targeted solutions, we can work towards creating a more equitable and prosperous society for all. Addressing poverty requires a sustained commitment from policymakers, community leaders, and individuals. Only through collaborative efforts can we hope to reduce poverty rates and improve the lives of millions of Americans.
Q&A:
- Q: What does the 'map of us poverty' show? A: It shows the geographical distribution of poverty rates across the United States, highlighting regional disparities.
- Q: Which region in the US has the highest poverty rates? A: The South consistently exhibits the highest poverty rates.
- Q: What are some key factors contributing to poverty? A: Lack of education, unemployment, healthcare costs, housing costs, and discrimination.
- Q: What are some potential solutions to address poverty? A: Investing in education, creating job opportunities, expanding access to healthcare, and increasing affordable housing.
- Q: How can technology help address poverty? A: By providing digital literacy training, telehealth services, and online education platforms.
Keywords: US Poverty Map, Poverty in America, Poverty Rates, Regional Disparities, Causes of Poverty, Poverty Solutions, Supplemental Poverty Measure, Official Poverty Measure, Affordable Housing, Job Creation, Education, Healthcare, Social Safety Net.













Poverty Line 2025 Ny Daniela Hope Fig 5 Ny Poverty Map Blue Poverty In The United States Mapped Vivid Maps Poverty By State Poverty Rate In The USA By State 1990 2024 Poverty Rate In The USA By State Persistent Poverty Identifying Areas With Long Term High Poverty Persistent Poverty Areas With Long Term High Poverty Figure 1 United States Poverty Ranking By State OC R MapPorn United States Poverty Ranking By State V0 Smqo6fdotz2a1 United States Poverty Map Ruth Cameron Poverty Map 2 U S Poverty Rate Varies By Age Groups Figure 1
Poverty In The States 2022 Scioto Analysis Supplemental Poverty Rate 2022 List Of U S States And Territories By Poverty Rate Wikipedia 1200px Poverty By U.S. State.svg Choropleth Map Of Poverty Throughout The United States With The Choropleth Map Of Poverty Throughout The United States With The Geographic Distribution Poverty Level 2024 By State Usa Dari Madlin State Official Poverty Rates Changed Over 10 Years Figure 1 Population Below Poverty Level By U S State FactsMaps Xxbelow Poverty 28336945 Poverty Guidelines 2025 Marketplace Charlotte H Bishop FPL 2023 1280x888 American Poverty Rate 2025 Louis M Proctor Poverty Min
U S Poverty Map Zw6o0tka6tb21 United States Poverty Map Ruth Cameron Persistent Poverty Areas With Long Term High Poverty Figure 2 American Poverty Rate 2025 Louis M Proctor US Poverty Map 2048x1221 United States Poverty Map Ruth Cameron Cb16 159 Poverty Map Poverty Level 2024 By State List Gusta Katrina Poorest States In America American Poverty Map Four Us Poverty Line 2025 Dorri Felicle PovertyByState Poverty In The United States 1100x850 R MapPorn PqIRqTkzLU7GVm ImQ1i0xtw2lhknU9aJ1Y5 AQCOc0
U S Poverty Rate Varies By Age Groups Figure 2 American Poverty Map Poverty Map Web 400w Us Poverty Vivid Maps Us Poverty 2048x1310 Poverty Line 2024 Usa Per Month Viv Lilith Poverty Data Thumbnail Poverty In America Statistics Poverty Rate Varies By Age Groups Figure 1 American Poverty Map Poverty Rates By Age County Region Figure 3 American Poverty Map 9091f711b478c2de76fb5b35e4cb6f527d483073
U S Poverty Rates Differ By Age And County Poverty Rates By Age County Region Figure 1 American Poverty Map C4184dc1e007c6662fd8f2e57e38f11a American Poverty Map Acs 5yr Poverty Rate All Counties

