Last update images today US Power Plants Map: Illuminating Energy In America
US Power Plants Map: Illuminating Energy in America
This week, the topic of US power plants maps is generating significant interest. Let's delve into why understanding the distribution and types of power plants across the United States is crucial for energy policy, environmental awareness, and infrastructure planning.
US Power Plants Map: A Visual Overview
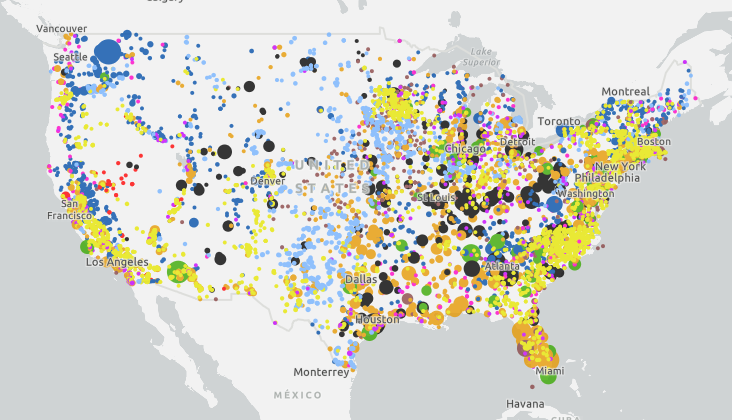
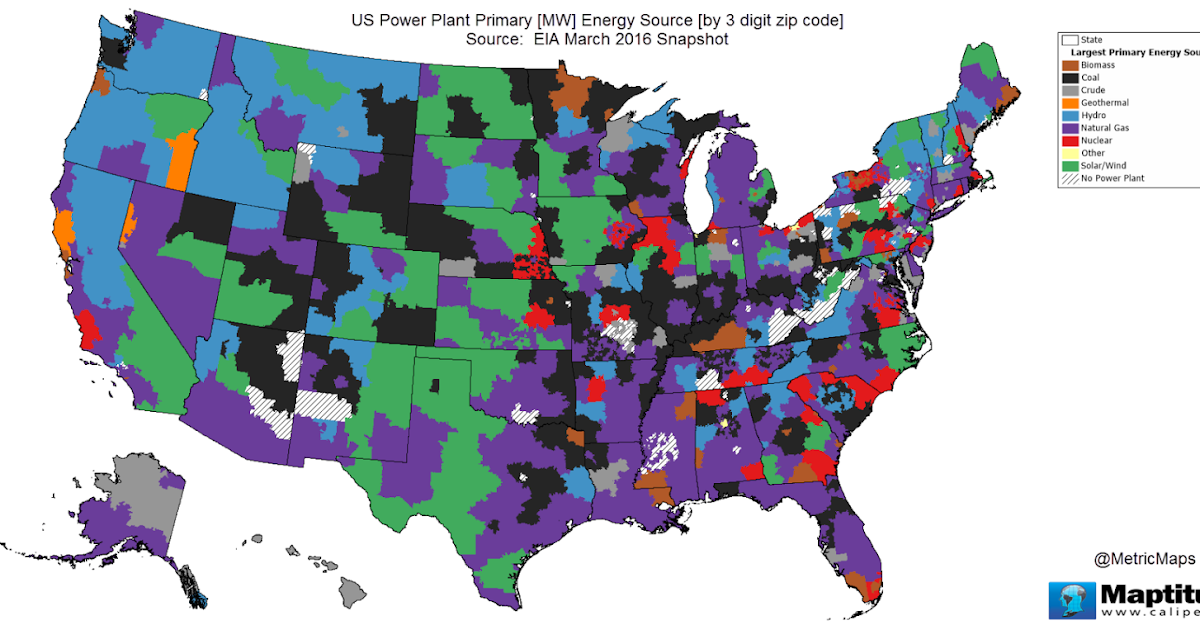
A US power plants map provides a visual representation of where power plants are located across the country. These maps often use color-coding or symbols to indicate the type of energy source the plant utilizes, such as coal, natural gas, nuclear, solar, wind, or hydroelectric.
- Target Audience: This article is intended for anyone interested in energy policy, environmental science, infrastructure, economics, government officials, and environmentally conscious citizens.
US Power Plants Map: Types of Power Plants
Understanding the different types of power plants is essential for interpreting a US power plants map. Here's a breakdown:
- Coal-fired Plants: These plants burn coal to heat water, creating steam that spins turbines connected to generators. They are a significant source of electricity but also contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Caption: A coal-fired power plant with smoke billowing from its stacks.
- Natural Gas Plants: Similar to coal plants, these use natural gas to generate steam. They generally produce fewer emissions than coal plants.
- Caption: A natural gas power plant at dusk.
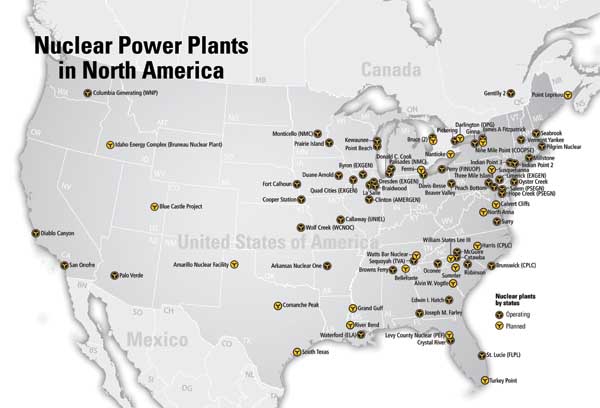
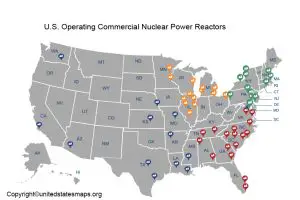
- Nuclear Power Plants: These plants use nuclear fission to generate heat, which then creates steam to turn turbines. Nuclear power is a low-carbon energy source but raises concerns about nuclear waste disposal and safety.
- Caption: A nuclear power plant with its iconic cooling towers.
- Hydroelectric Power Plants: These plants use the force of flowing water to spin turbines. Hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source, but dam construction can have environmental impacts on river ecosystems.
- Caption: A hydroelectric dam with water flowing through its turbines.
- Solar Power Plants: These plants use photovoltaic (PV) cells to convert sunlight directly into electricity or use concentrated solar power (CSP) technologies to focus sunlight and generate heat. Solar power is a renewable and clean energy source, but its availability depends on sunlight.
- Caption: A large-scale solar farm stretching across the landscape.
- Wind Power Plants: Also known as wind farms, these consist of numerous wind turbines that convert wind energy into electricity. Wind power is a renewable energy source, but its availability depends on wind conditions, and it can sometimes face opposition due to visual impact and noise.
- Caption: A wind farm with turbines spinning against a blue sky.
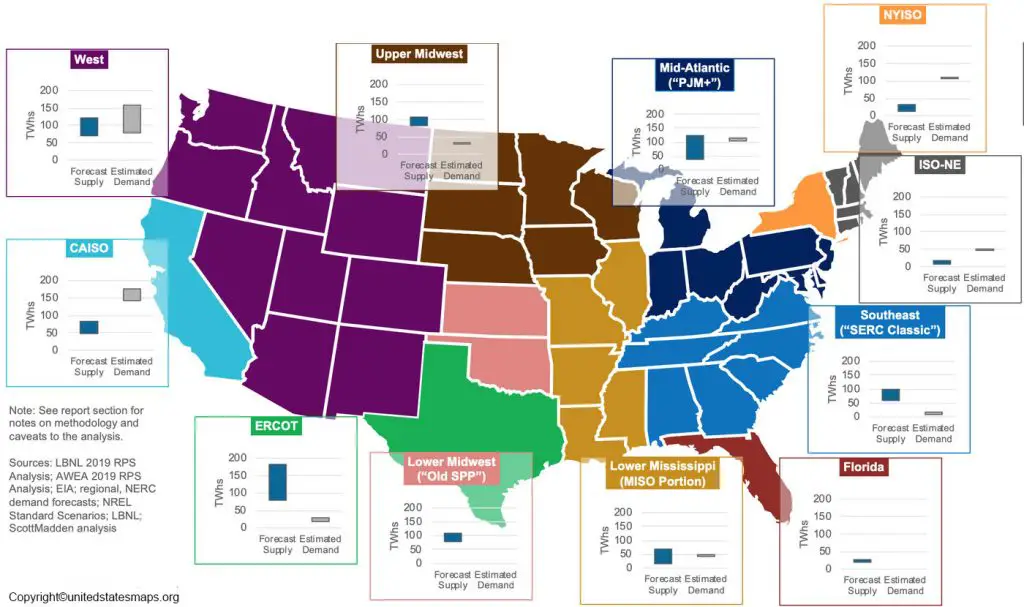
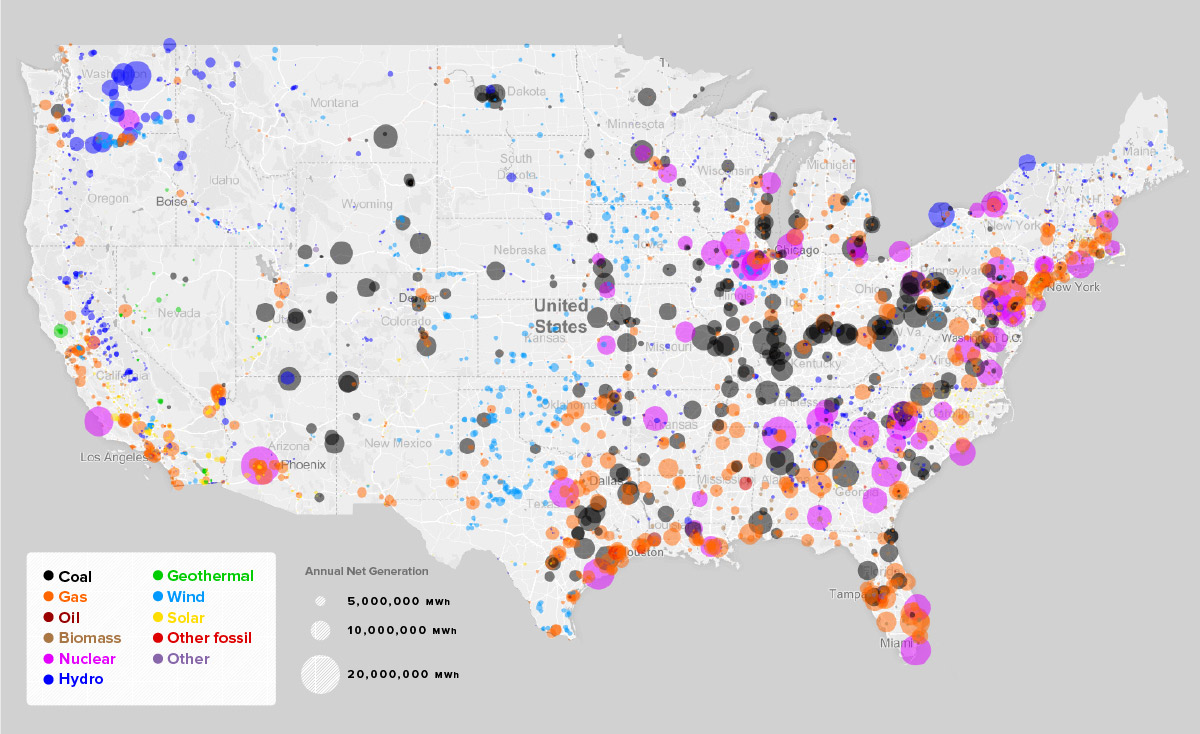
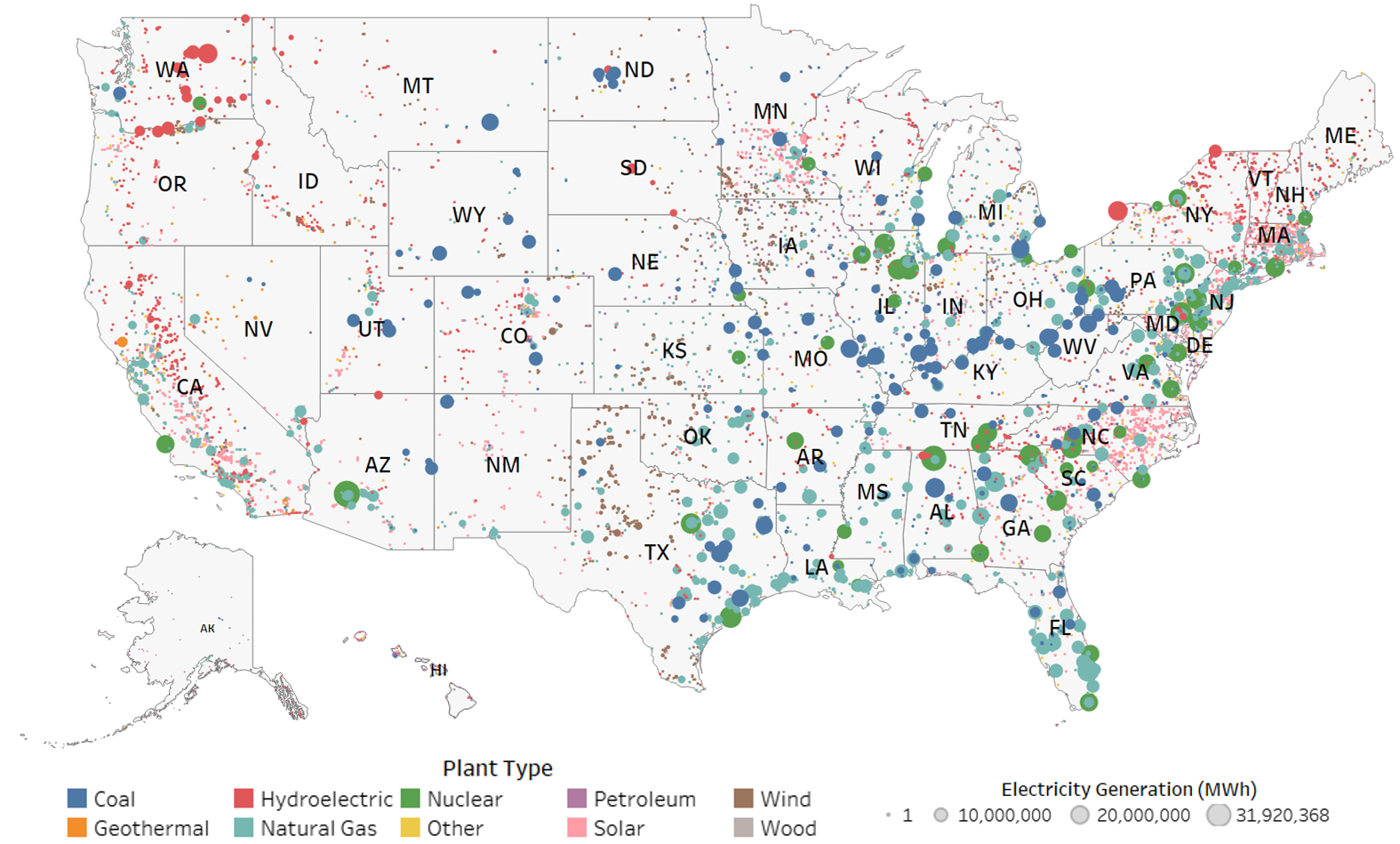
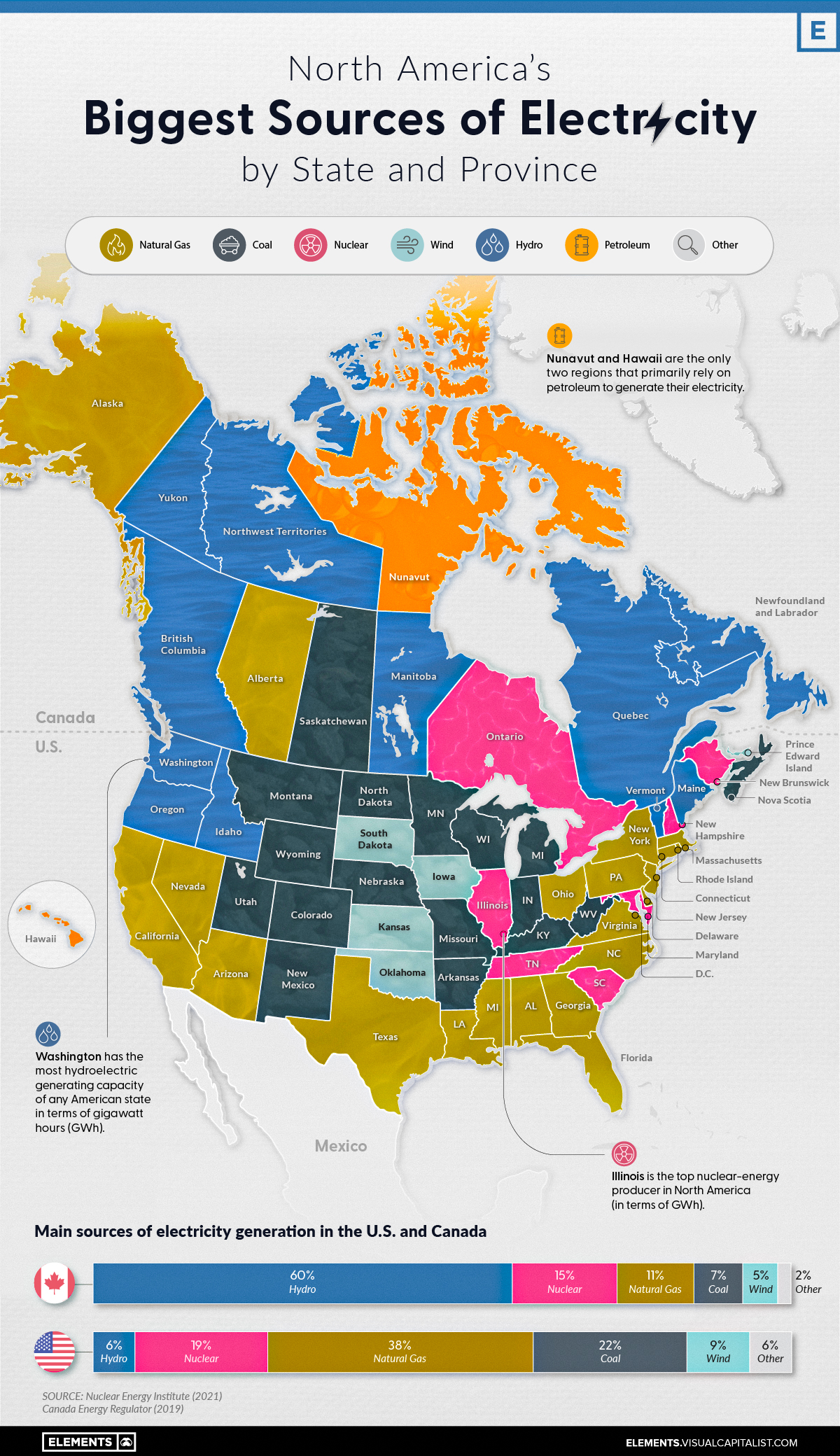
US Power Plants Map: Geographic Distribution
The distribution of power plants across the US is not uniform and is influenced by factors such as resource availability, population density, and regulatory policies.
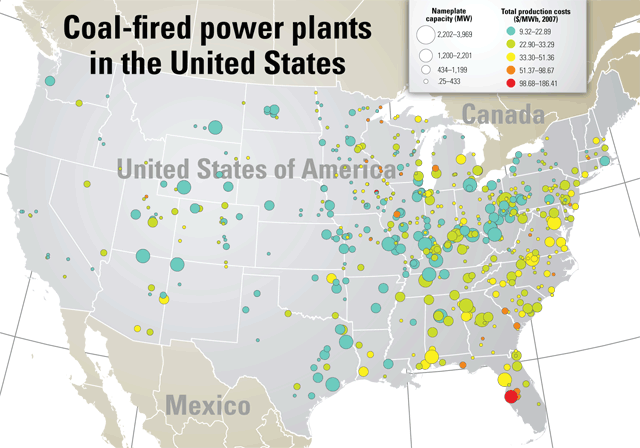
- Coal-fired plants are concentrated in regions with abundant coal reserves, such as the Appalachian Mountains and the Midwest.
- Natural gas plants are common in areas with natural gas production, such as Texas, Pennsylvania, and Louisiana.
- Hydroelectric plants are prevalent in mountainous regions with significant rivers, such as the Pacific Northwest and the Southeast.
- Solar power plants are increasingly common in sunny regions, such as the Southwest and California.
- Wind power plants are concentrated in the Great Plains and coastal areas with strong winds.
- Alt Text: US Power Plants Map illustrating geographical distribution.
US Power Plants Map: Importance and Applications
Understanding the US power plants map has several important applications:
- Energy Policy: Policymakers use this information to develop strategies for energy production, distribution, and conservation.
- Environmental Planning: Environmental agencies use the map to assess the environmental impacts of power plants and develop regulations to minimize pollution.
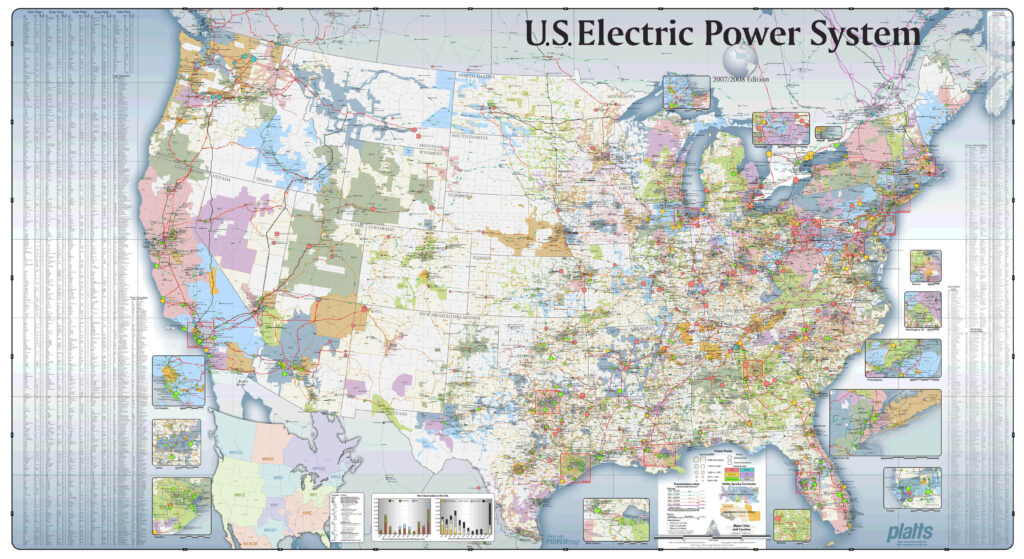
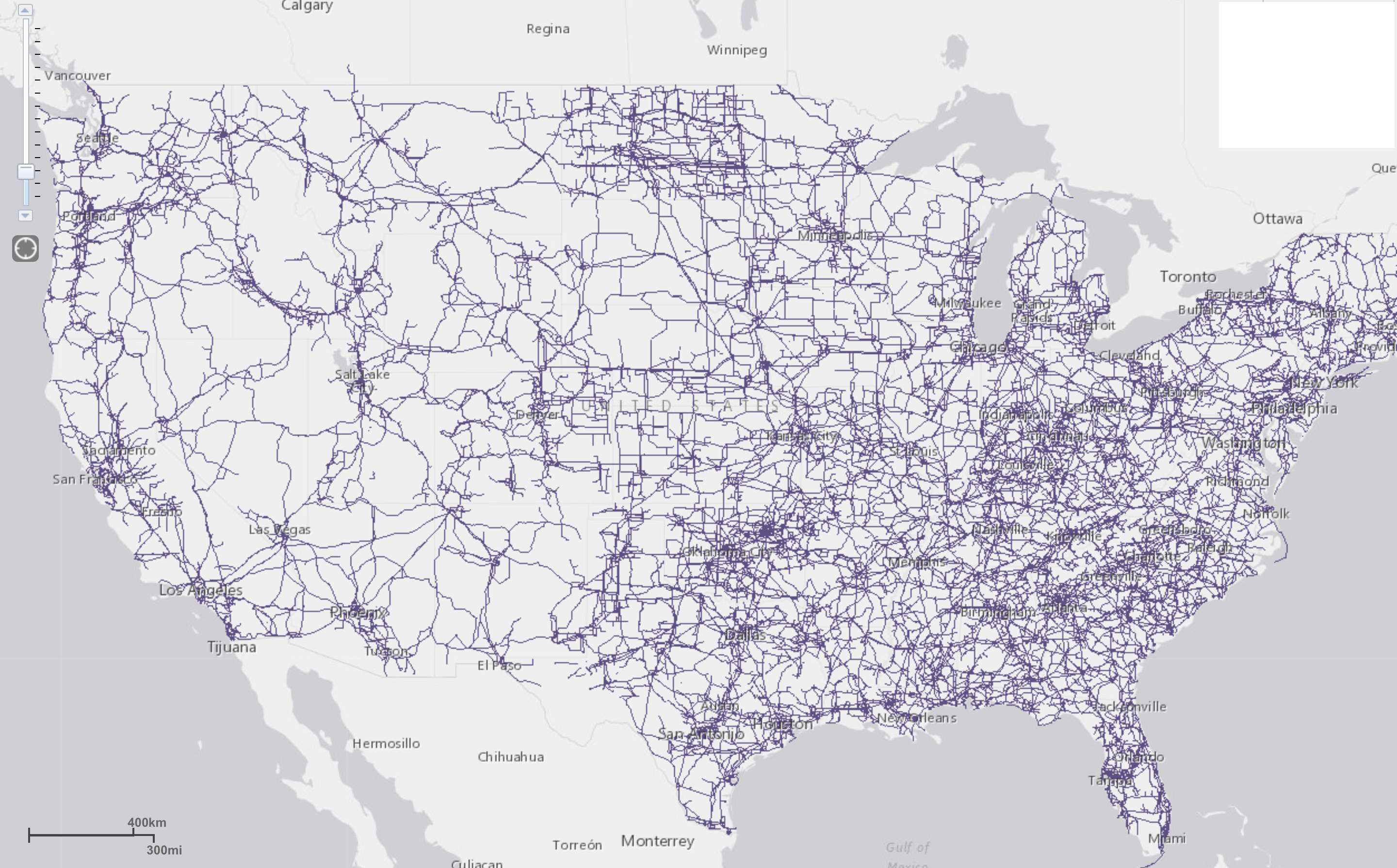
- Infrastructure Planning: Utility companies use the map to plan the construction and maintenance of transmission lines and other infrastructure.
- Economic Development: Businesses and communities use the map to identify opportunities for energy-related investments and economic development.
- Emergency Response: During natural disasters or other emergencies, the map helps emergency responders understand the location of critical energy infrastructure.
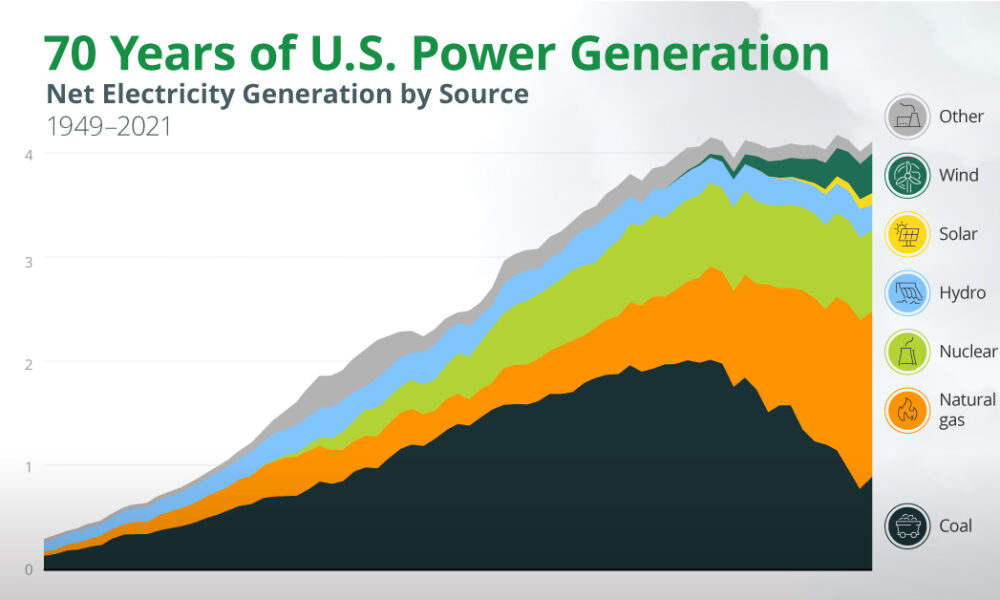
US Power Plants Map: Recent Trends
Several trends are shaping the US power plant landscape:
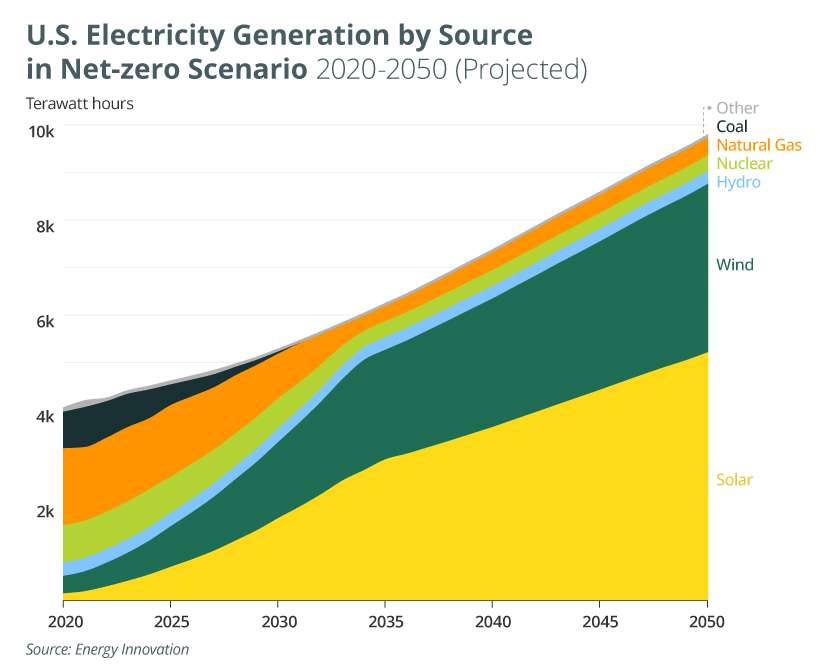
- Shift to Renewable Energy: There's a growing trend towards renewable energy sources like solar and wind, driven by environmental concerns and declining costs.
- Retirement of Coal Plants: Many older coal-fired plants are being retired due to environmental regulations and competition from cheaper natural gas and renewable energy.
- Expansion of Natural Gas: Natural gas is playing an increasingly important role as a bridge fuel, providing a cleaner alternative to coal while renewable energy scales up.
- Grid Modernization: Efforts are underway to modernize the electrical grid to improve its reliability, efficiency, and ability to integrate renewable energy sources.
US Power Plants Map: Accessing the Data
Several sources provide data and maps of US power plants:
- U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA): The EIA is the primary source of energy data and analysis for the US government. They provide detailed information on power plant locations, types, and capacities.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): The EPA provides data on the environmental performance of power plants, including emissions and waste management.
- OpenStreetMap: This collaborative mapping project includes data on power plants contributed by volunteers.
- Commercial Data Providers: Several companies offer specialized data and mapping services for the energy industry.
-
Q: Where can I find a detailed map of US power plants?
- A: The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) website is the best source for comprehensive power plant data and maps.
-
Q: What types of power plants are most common in the US?
- A: Natural gas power plants are currently the most common, followed by coal, nuclear, and renewable energy sources like hydro, wind, and solar.
-
Q: Why are some coal plants being retired?
- A: Coal plants are being retired due to stricter environmental regulations, increased competition from cheaper natural gas and renewable energy, and aging infrastructure.
-
Q: Are renewable energy sources becoming more prevalent in the US?
- A: Yes, renewable energy sources like solar and wind are growing rapidly in the US, driven by environmental concerns, technological advancements, and declining costs.
-
Q: How does the US power plants map impact environmental policy?
- A: The map helps policymakers understand the distribution of polluting power plants and develop targeted regulations to reduce emissions and protect air and water quality.
-
Q: Is a map important?
- A: Yes, maps are important because they can aid policymakers in energy production, distribution and conservation.
Keywords: US Power Plants Map, Energy Policy, Renewable Energy, Coal Plants, Natural Gas Plants, Solar Power, Wind Power, EIA, EPA, Energy Infrastructure, Grid Modernization.
Summary Question and Answer: The US Power Plants Map is vital for understanding energy distribution and types in America, crucial for energy policy and environmental awareness. Key trends include a shift to renewable energy and the retirement of coal plants. The EIA is a primary source for detailed maps.














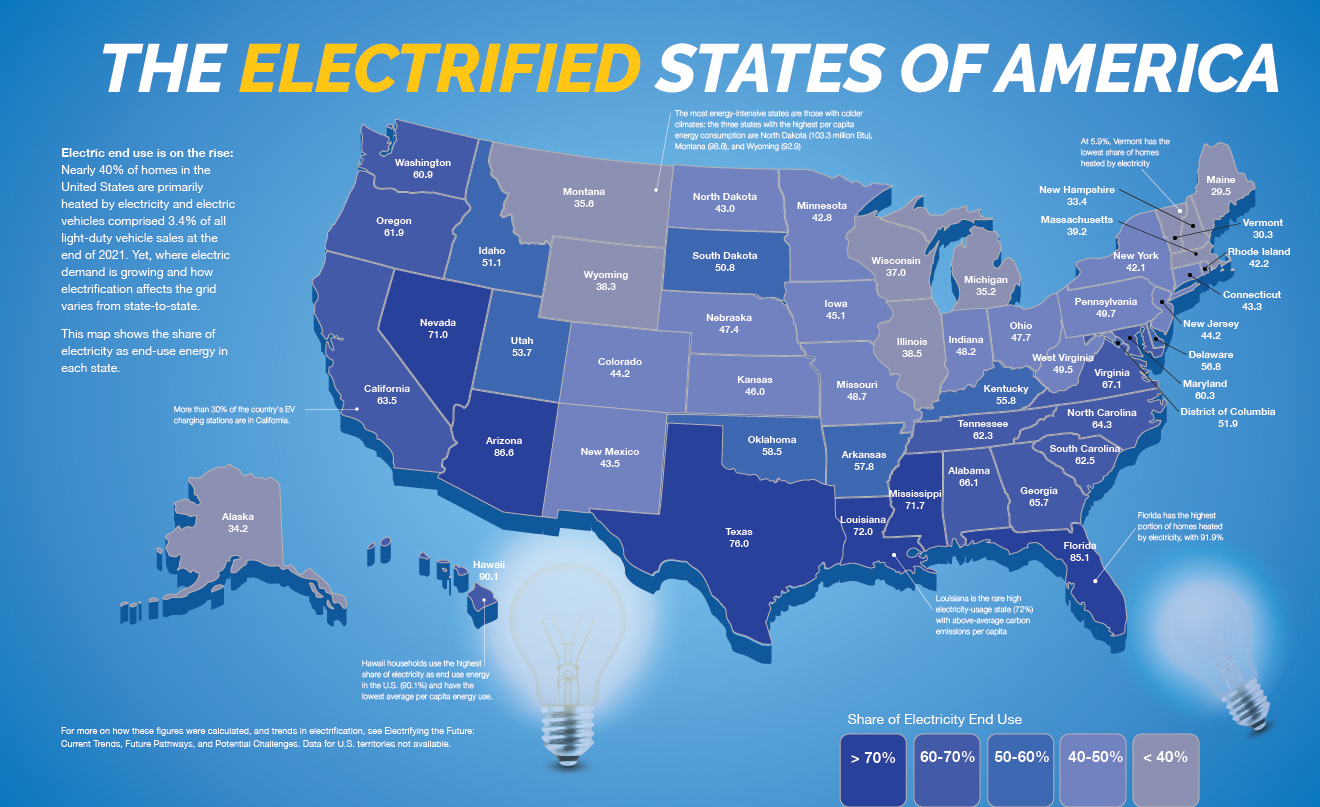
Interactive Map Of U S Power Plants Synapse Energy USPowerPlantMapCard Chart Nearly All New U S Power Plants Built In 2024 Will Be Clean 22023202420canary20media Coal In The United States 520004dd9936c 64 Coal Fired Map A Visual Guide To Nuclear Power In The United States Understanding The 520004db51ef8 110109 IndTrends Map Which U S Utilities Have The Cleanest Electricity Generation SHAREABLE NPUC US Power Generation 08022023 01 1000x600 Nuclear Power Plants Map Us Power Plants Map US Nuclear Power Plants Map USA Nuclear Power Plants Map Us Nuclear Power Plants Map 300x200
Renewable Energy Power Plants Active Under Construction And Planned Renewable Energy Power Plants Active Under Construction And Planned By Energy Sector Q320 Map Of Nuclear Power Plants In The U S This Is Where Reactors Are Map This Interactive Map Shows US Electricity Usage In Real Time World Xj8xZ70sq TVyA ZK3axV6T5l8ZFOQrbt16mWYcjPjM.PNGMapping The Leading Electricity Sources In The US And Canada Biggest Sources Of Electricity Usa Canada State Province A Visual Guide To Nuclear Power In The United States Understanding The Map Of 65 Currently Operating US Nuclear Power Plants And The States A Whose Statutes Power Grid Map Of US United States Maps Us Power Grid Map 1024x607 The Electrified States Of America American Public Power Association PPM September October 2022 Electrification Map Graphic Full 70 Years Of U S Electricity Generation Motive Power NPUC US Power Generation 08022023 01
Is There Going To Be A Power Outage In 2025 Rita L King Us Power Outages Increase Power Grid Map USA Printable Map Of USA Us Electric Power System Map System Map Electricity Power Grid 1024x559 Coal Fired Power Plants Across The U S Source Download Coal Fired Power Plants Across The US Source Map Of Us Coal Power Plants Almeta Mallissa 520004db2e984 100110 IndustryTrendsMap Short Term Energy Outlook U S Energy Information Administration EIA Supp1 Electric Power Plants And Emissions Epp Map 2019 A Breakdown Of The Major Power Plants In Blackout Plants USA Power Plant Primary Energy Source US Energy
Mw 2025 Maps Karil Marlena Image Geothermal Power Plant Map Renewables Mapping How The United States Generates Its Electricity Map Power 93b791c15906390af2a22b47bd511be6 US Over 10 New Battery Plants To Be Launched In 2022 2025 New Battery Plants Us October 25 2021 Source Energygov Map Of The Us Power Grid 2024 Schedule 1 Screen Shot 2018 06 17 At 12.55.41 PM Nuclear Power Plants Map Tab1large ArcGIS Hub Data
US Nuclear Power Plants Map USA Nuclear Power Plants Map Usa Nuclear Power Plant Map US Nuclear Power Plants Map USA Nuclear Power Plants Map Usa Nuclear Power Plants Map 300x173

