Last update images today Unveiling The US Landscape: A Physical Map Guide
Unveiling the U.S. Landscape: A Physical Map Guide
This article delves into the diverse physical features of the United States, offering a comprehensive look at its mountains, plains, rivers, and more. Perfect for students, travelers, and geography enthusiasts!
The Alluring Physical Map of US: A Land of Contrasts
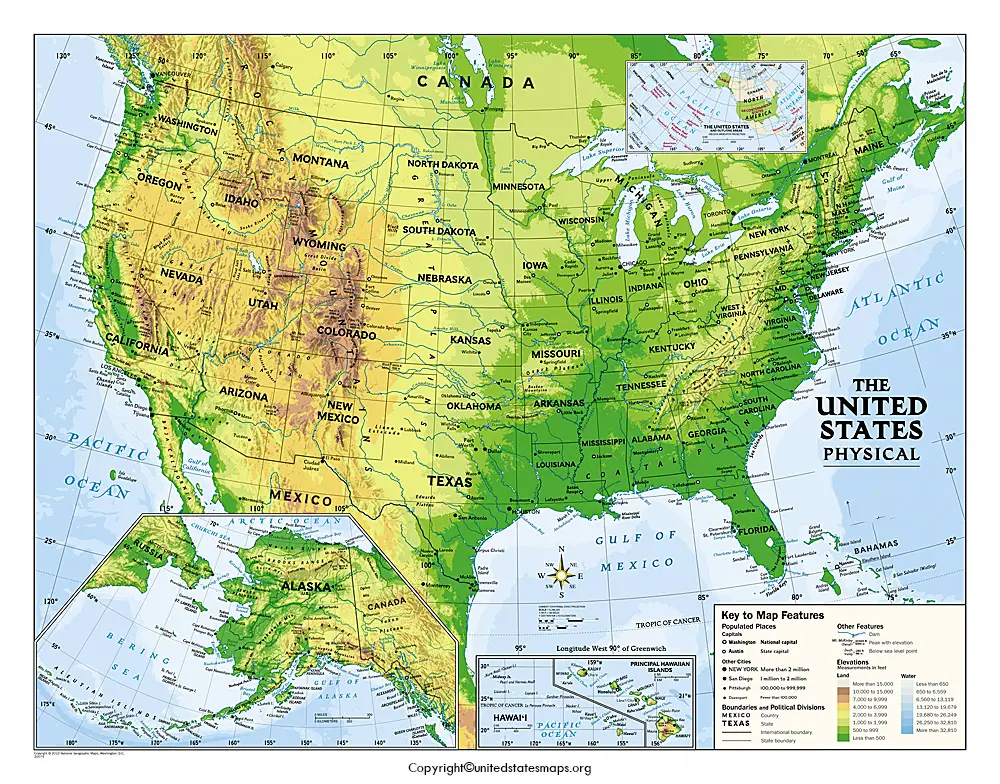
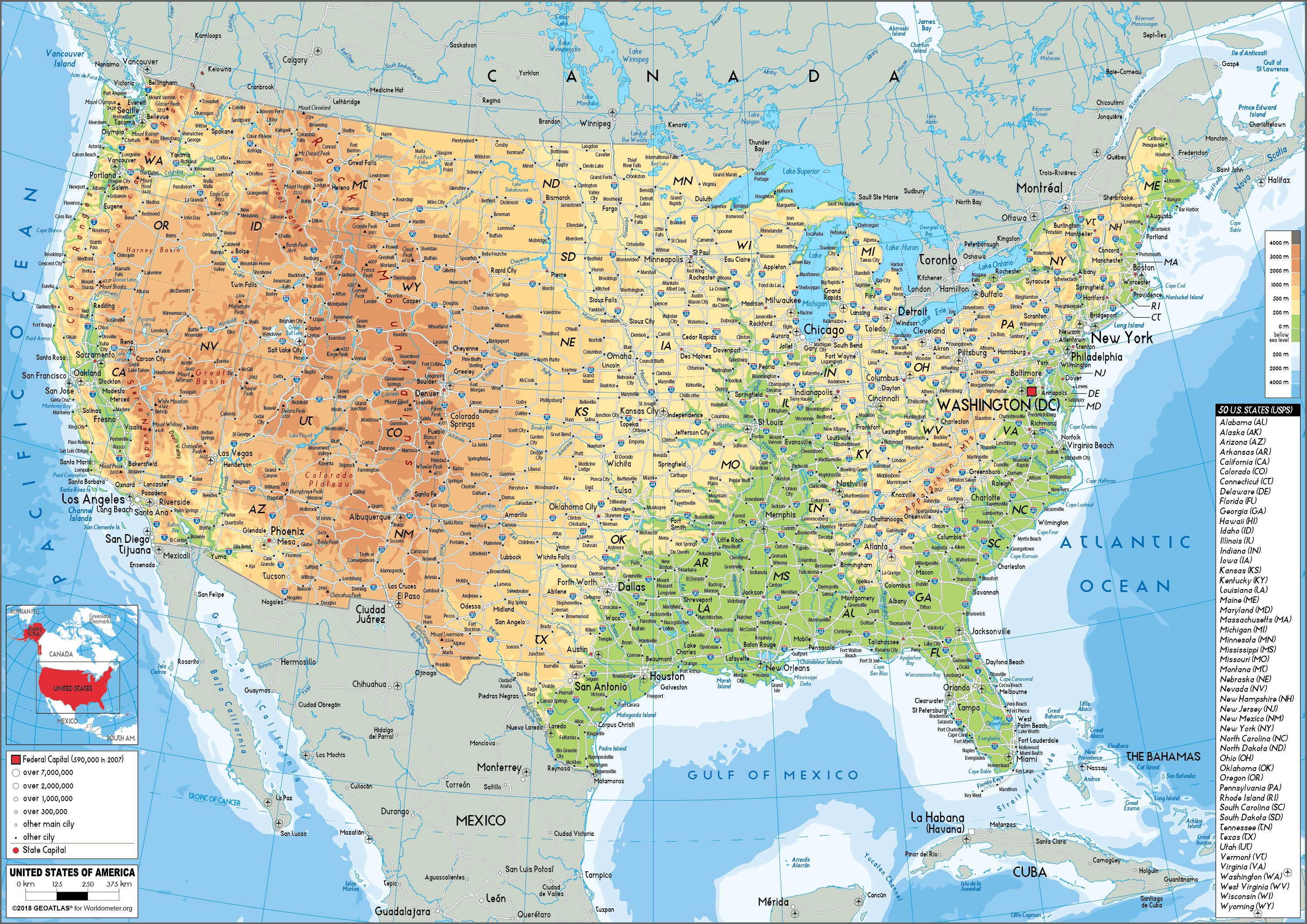
The United States boasts an incredibly varied landscape, from the towering peaks of the Rocky Mountains to the sprawling Great Plains and the sandy beaches of its coastlines. Understanding the physical map of the US is crucial for appreciating its environmental diversity, climate patterns, and even its economic activities. This article will guide you through the major physical features, providing insights into their formation and significance.
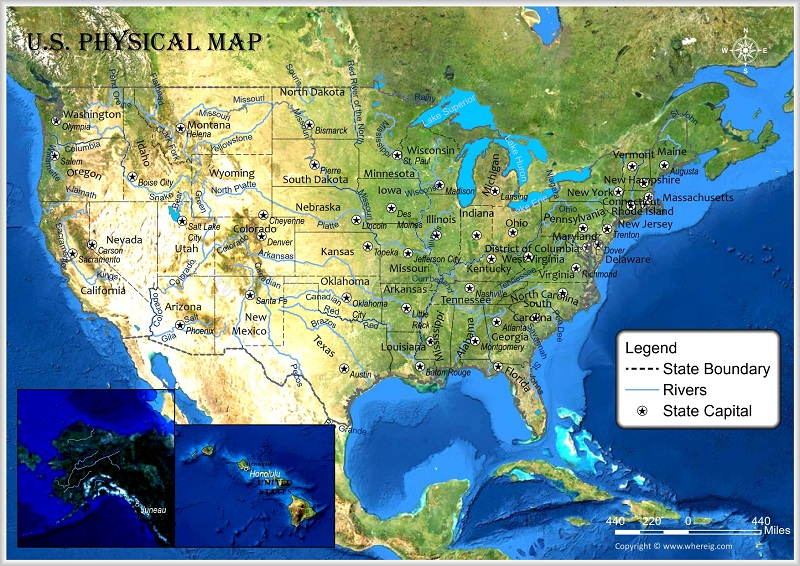
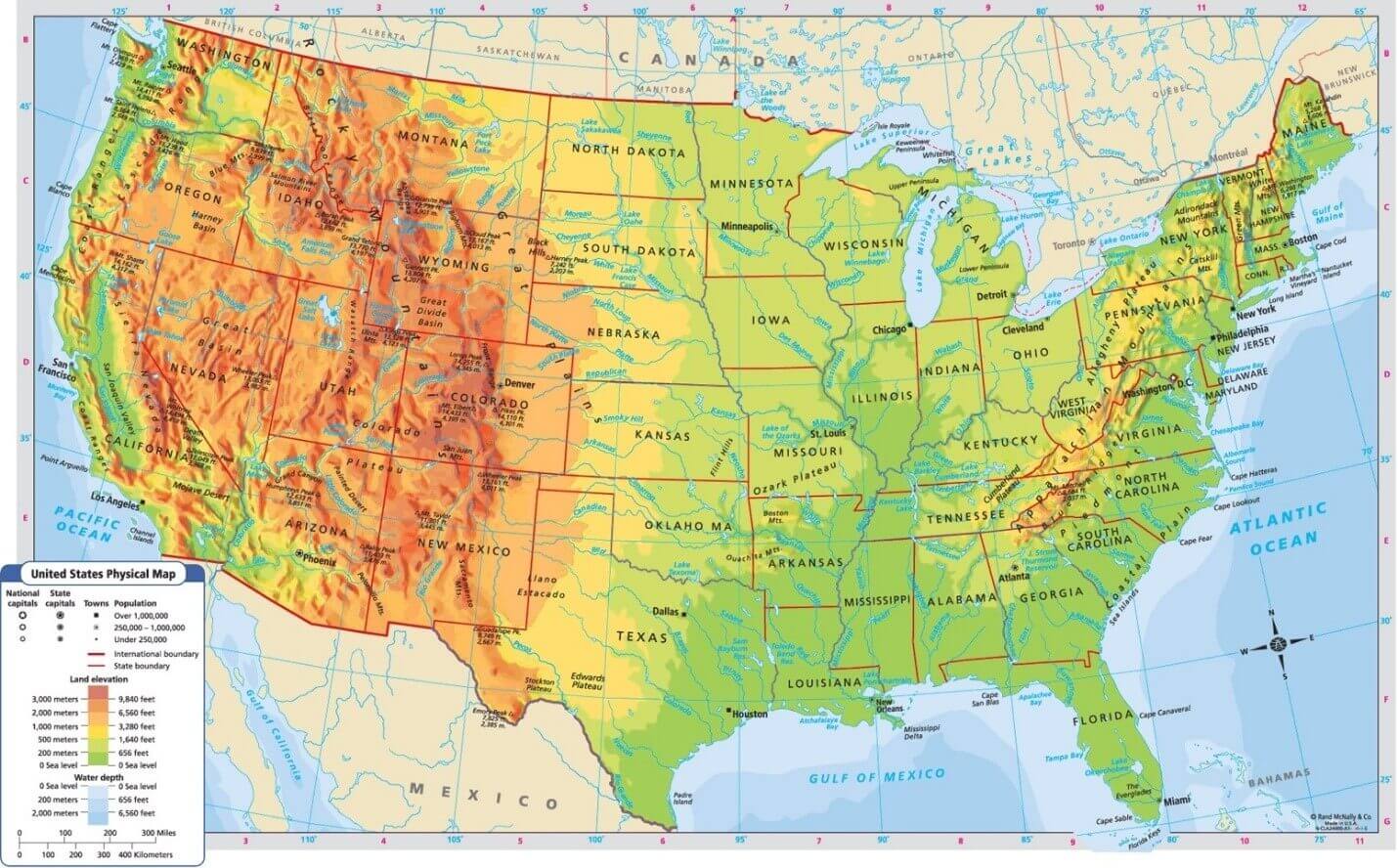
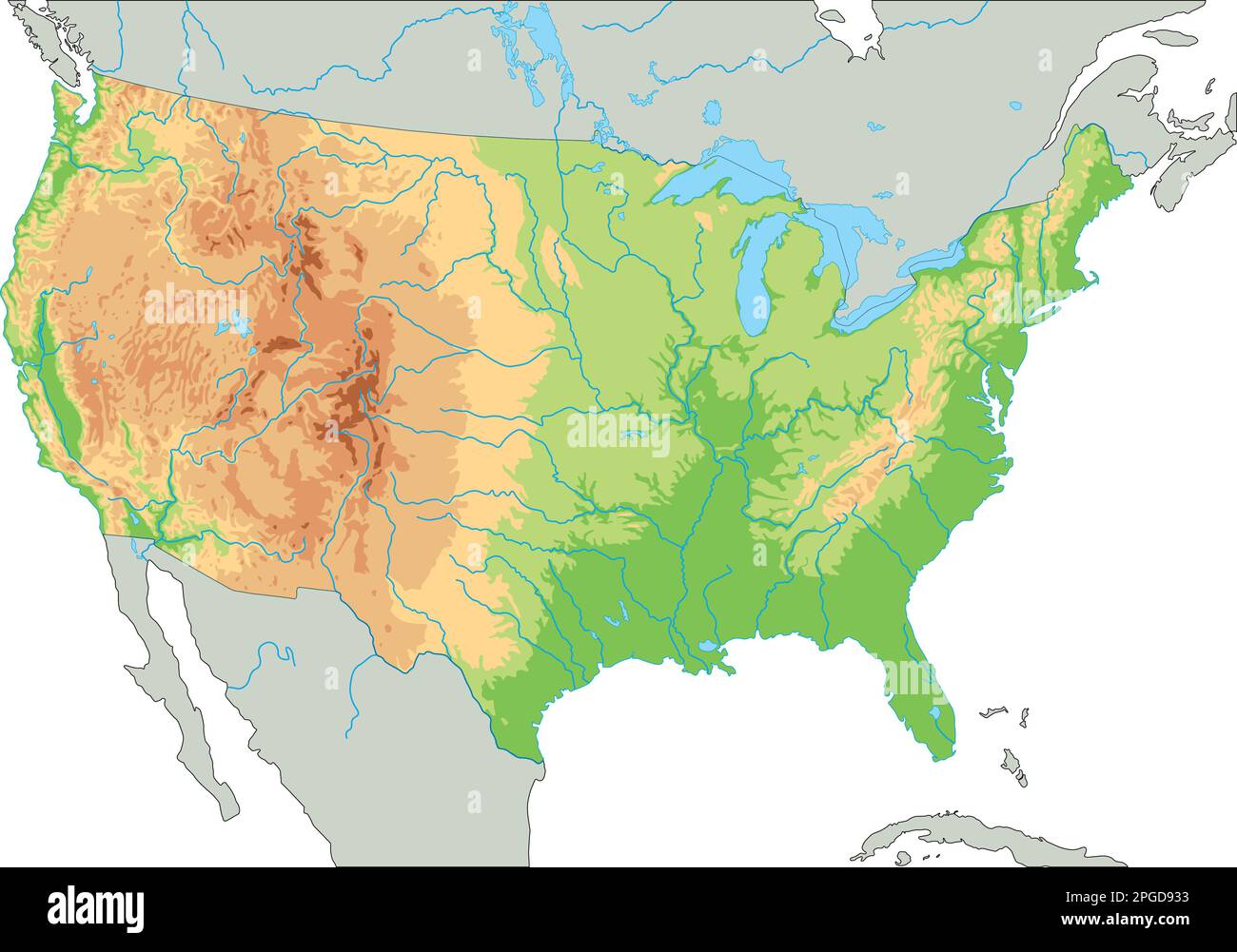
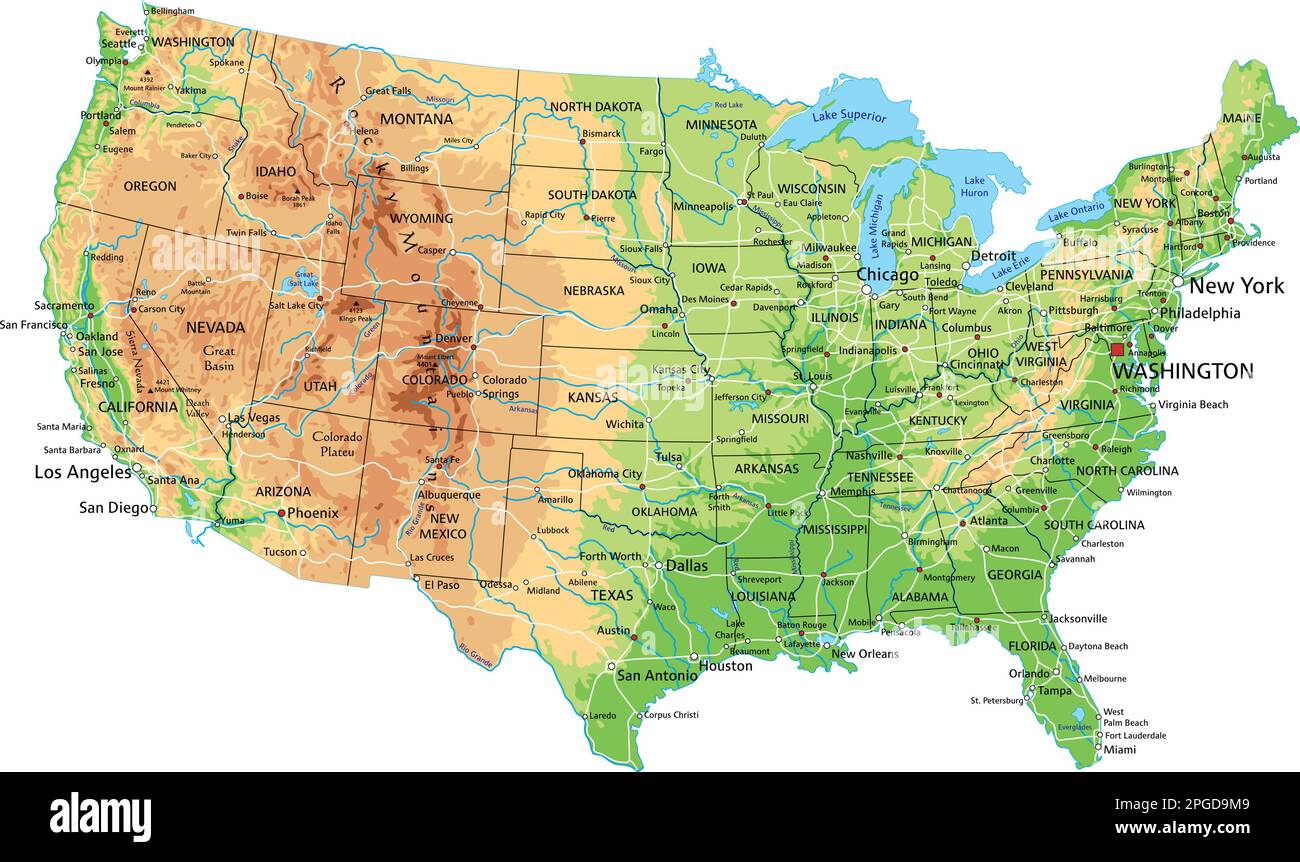
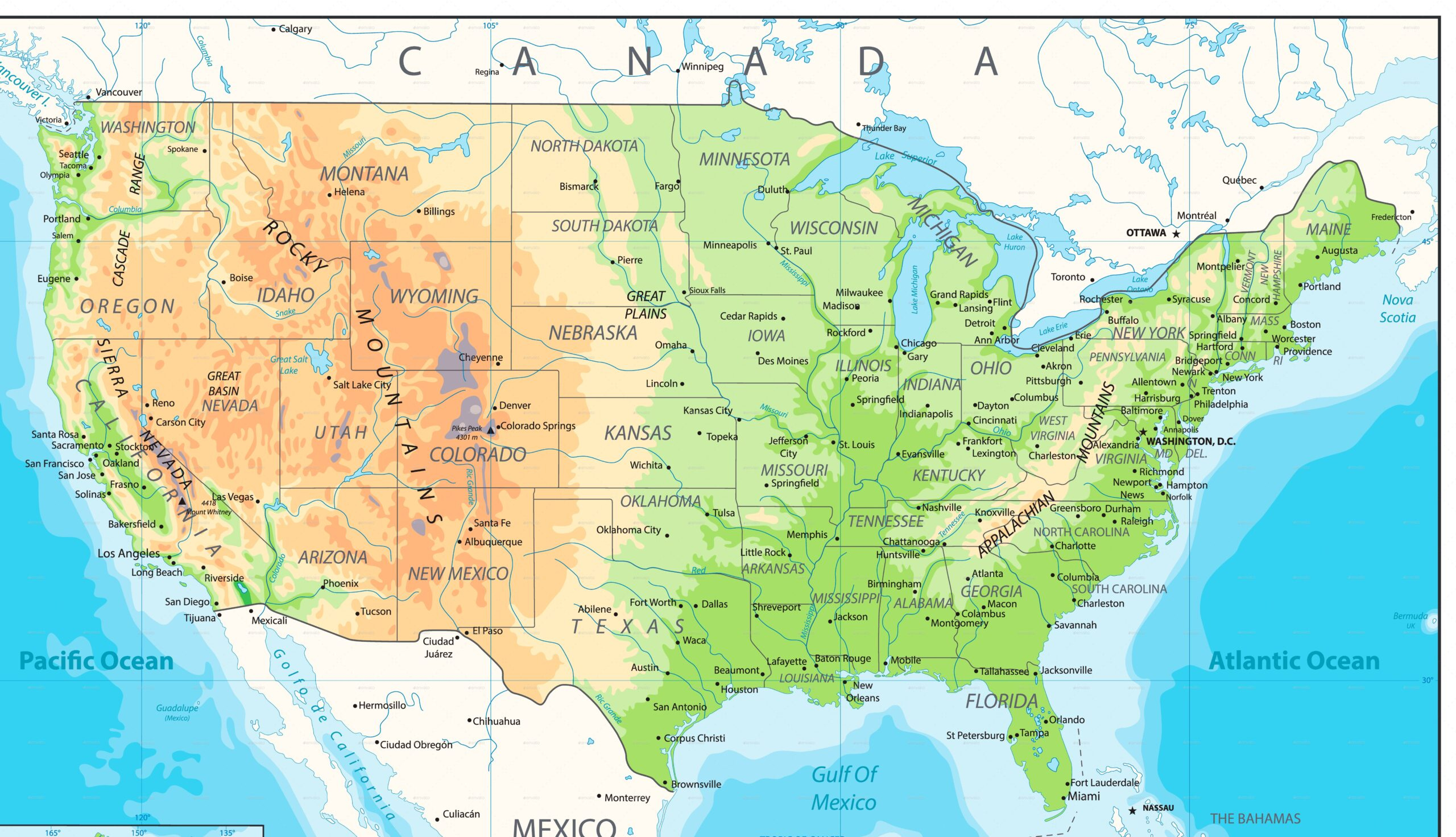
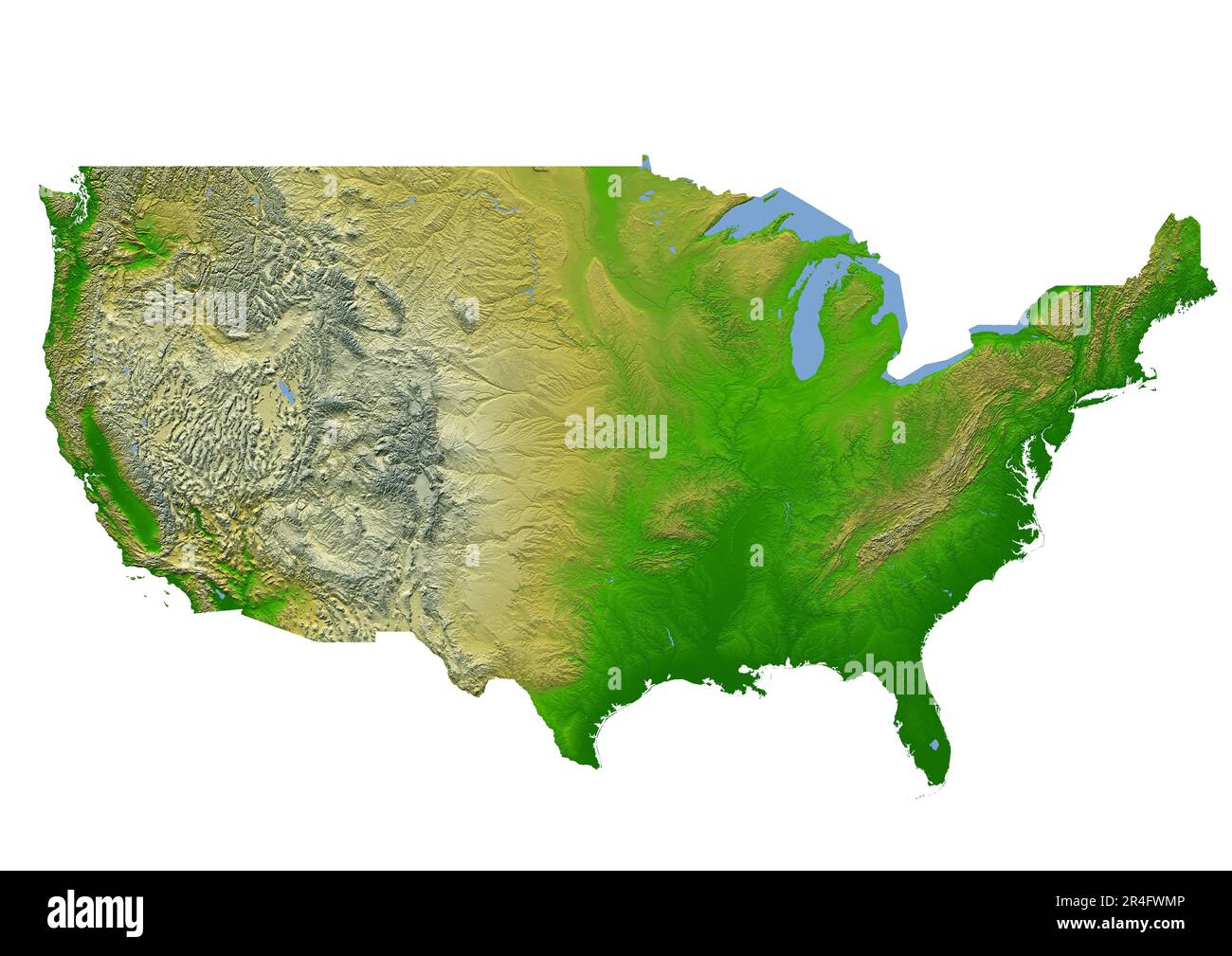
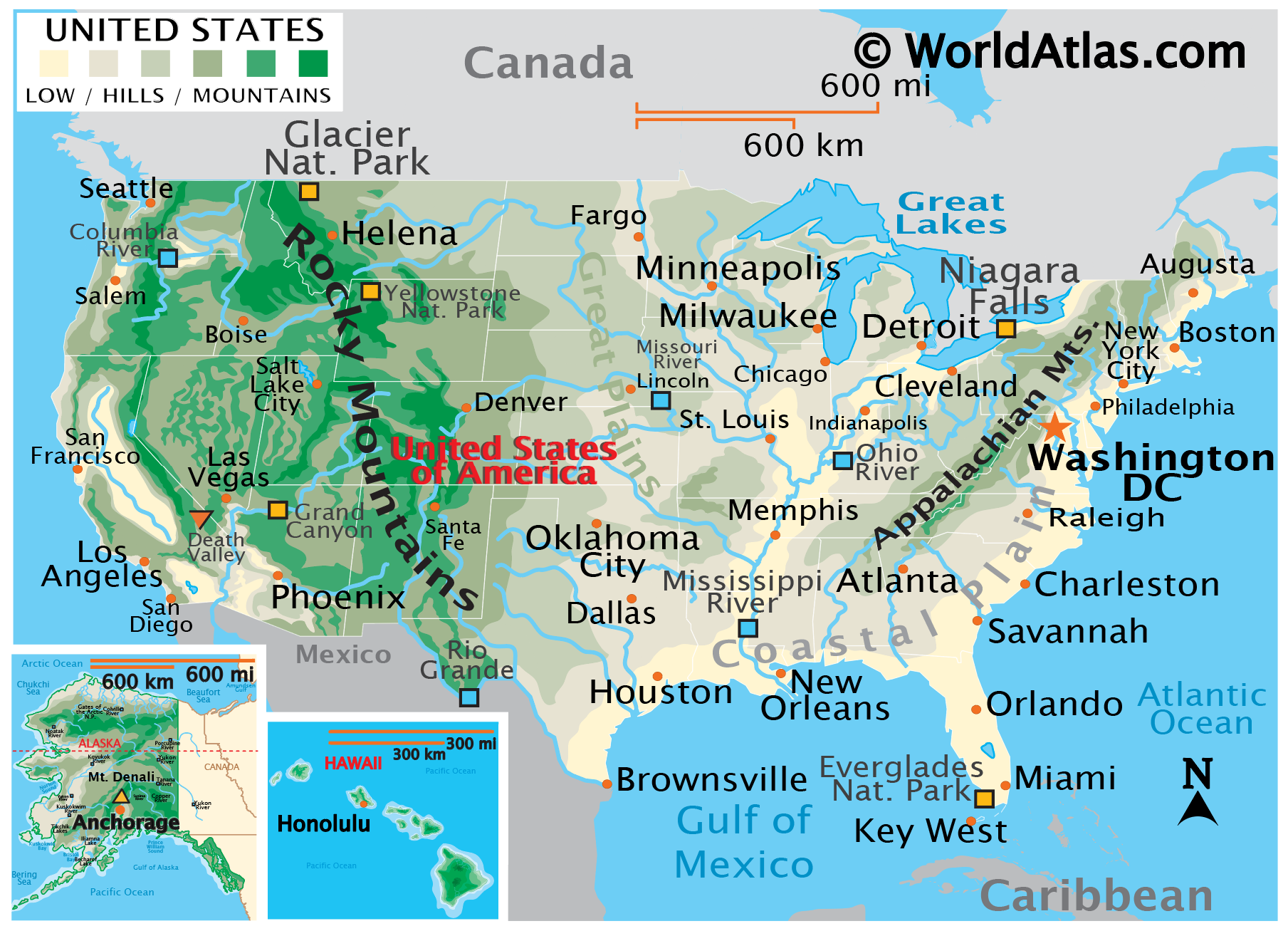
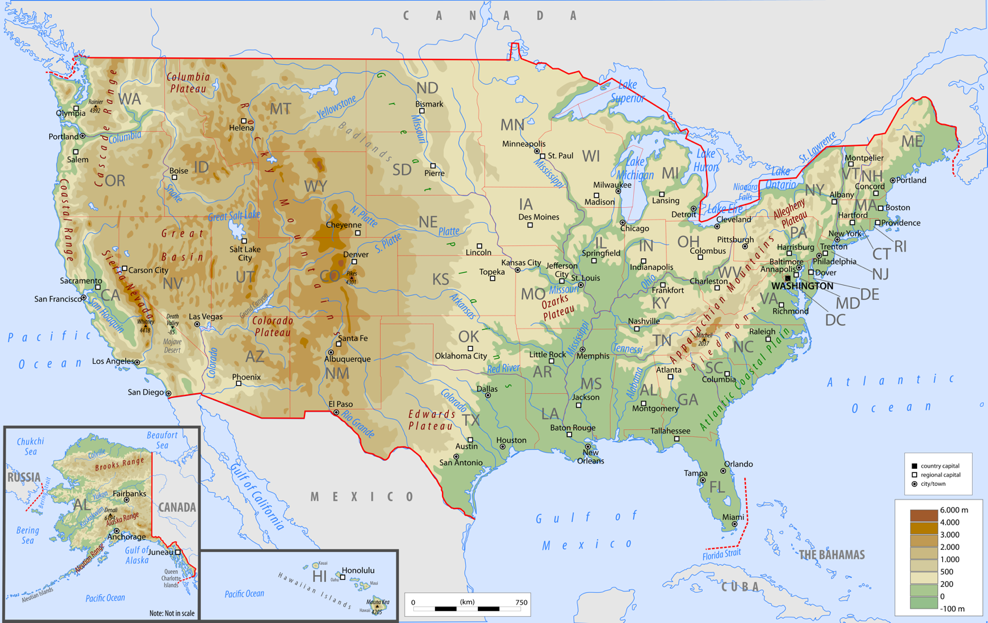
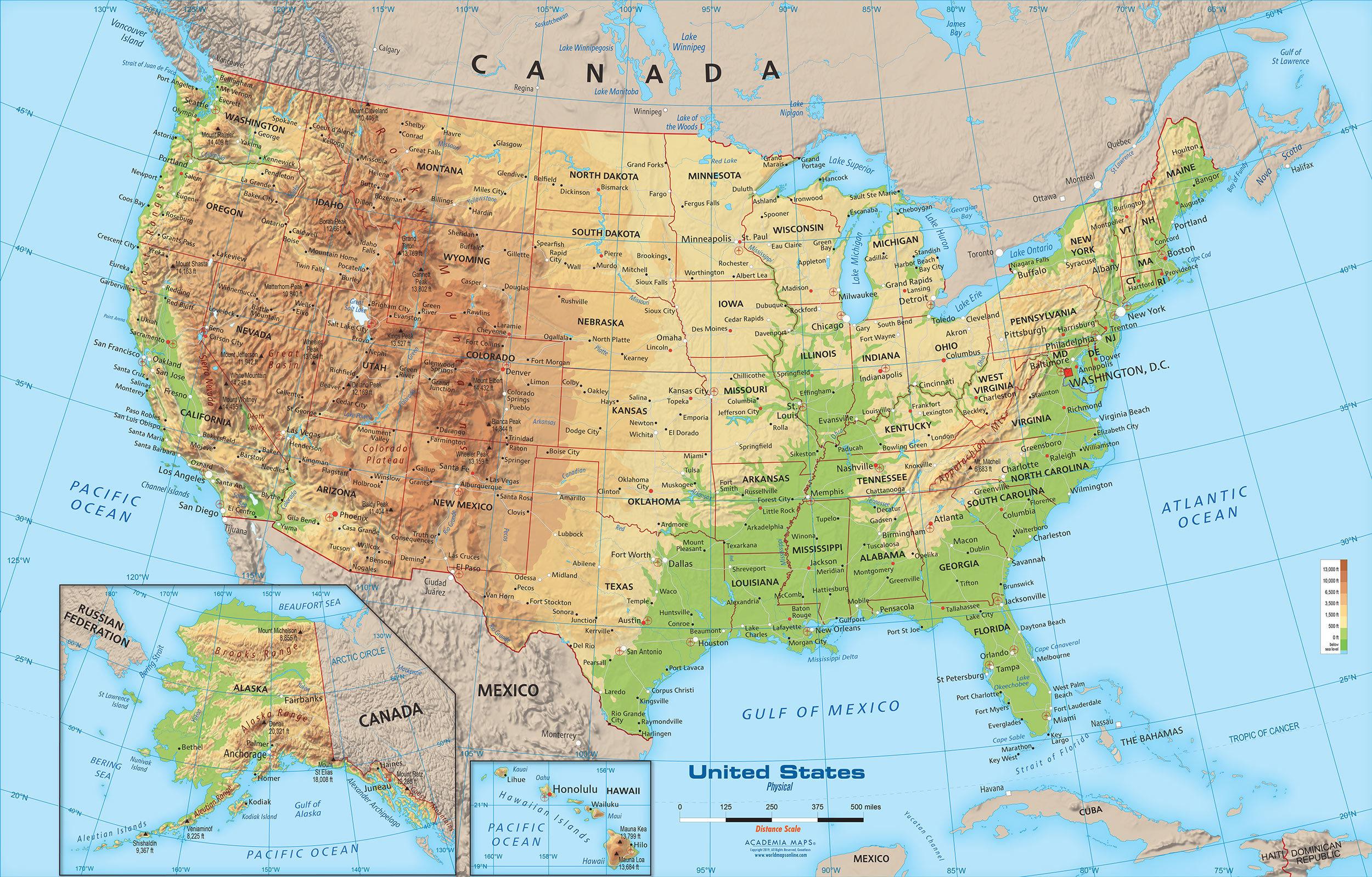
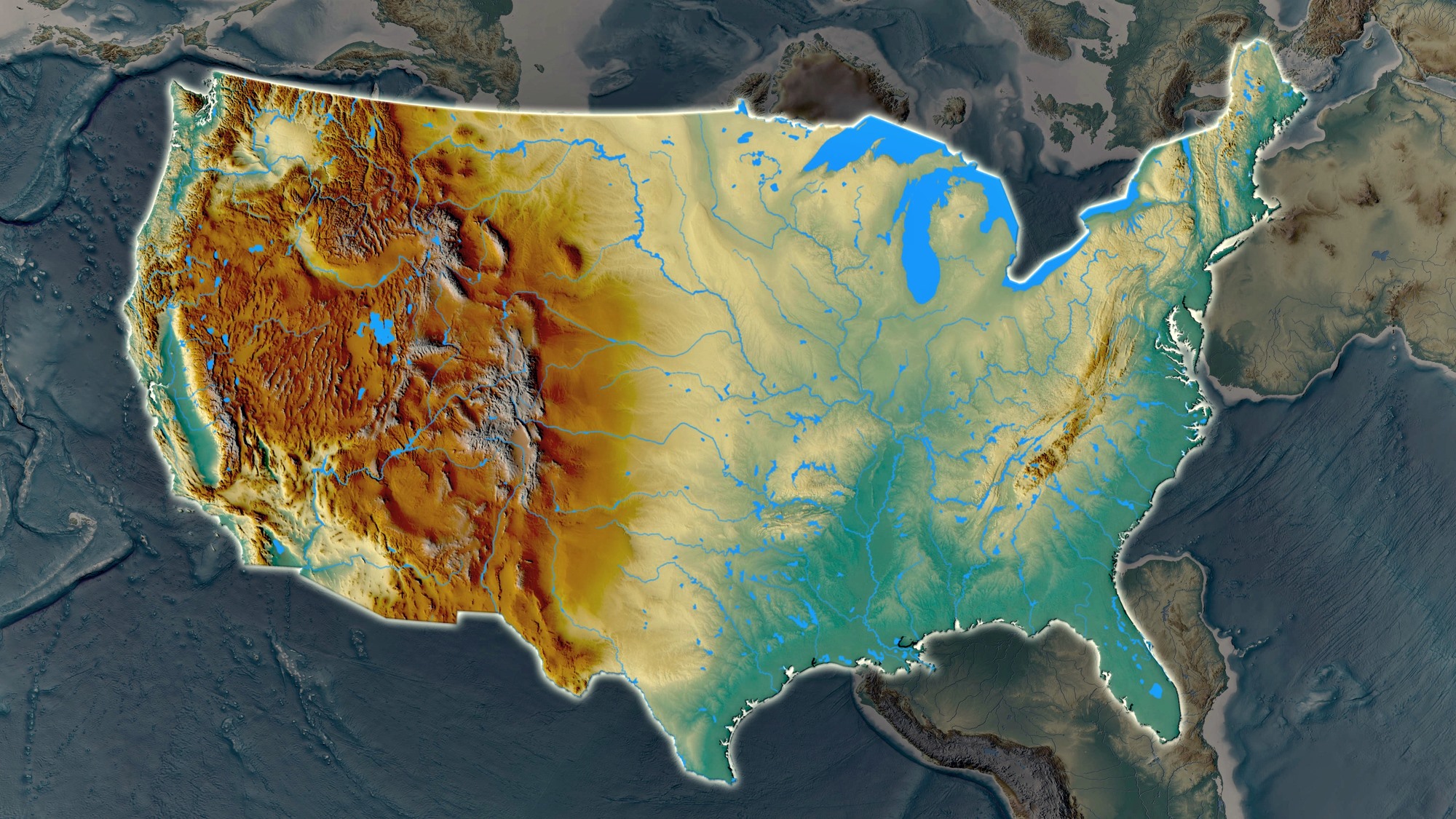
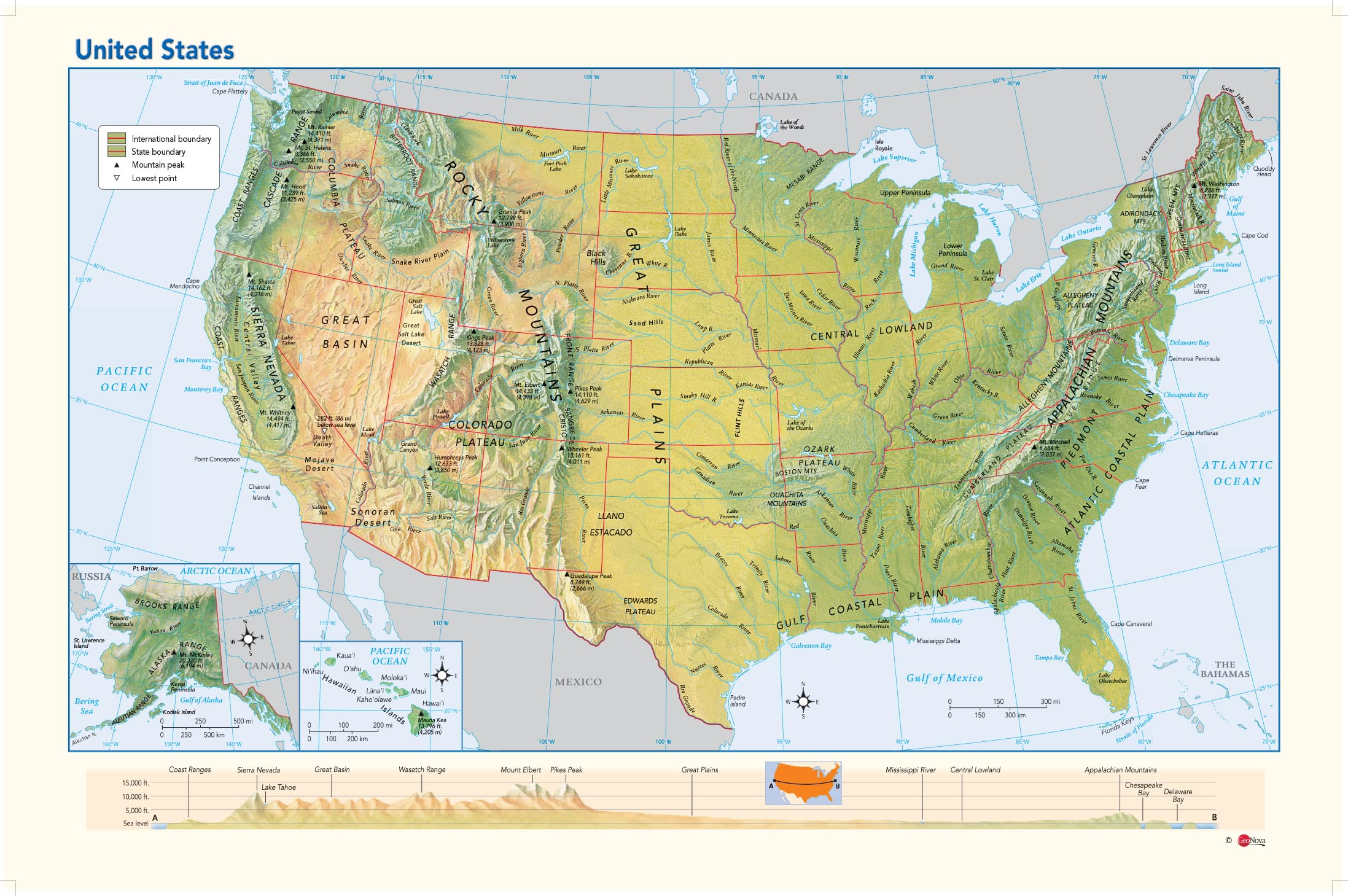
[Image of a physical map of the United States, showcasing elevation and major geographical features] Caption: A detailed physical map highlighting the diverse topography of the United States. Alt text: United States Physical Map
Exploring the Mountains: Shaping the Physical Map of US
Mountains dominate significant portions of the US landscape. The two major mountain ranges are the Appalachian Mountains in the east and the Rocky Mountains in the west.
-
Appalachian Mountains: These ancient mountains, much older and more eroded than the Rockies, stretch from Maine to Alabama. While not as tall as the Rockies, they feature rolling hills, forested ridges, and fertile valleys. They played a crucial role in early American history, acting as a barrier to westward expansion.
[Image of the Appalachian Mountains] Caption: The rolling, forested hills of the Appalachian Mountain range. Alt text: Appalachian Mountains
-
Rocky Mountains: A much younger and more rugged mountain range, the Rockies extend from Canada through the western US, ending in New Mexico. They are characterized by sharp peaks, deep valleys, and numerous national parks, including Yellowstone and Glacier. The Rockies are rich in minerals and serve as a vital source of water for the western states.
[Image of the Rocky Mountains] Caption: Snow-capped peaks of the majestic Rocky Mountains. Alt text: Rocky Mountains
-
Other Notable Mountain Ranges: The Cascade Range in the Pacific Northwest, known for its volcanoes (like Mount Rainier and Mount St. Helens), and the Sierra Nevada in California, home to Yosemite National Park and Mount Whitney (the highest point in the contiguous US), also significantly contribute to the US physical map.
The Expansive Plains: Defining the Physical Map of US
Between the Appalachian and Rocky Mountains lies the vast expanse of the Great Plains. This region is characterized by its flat, open grasslands and fertile soil, making it ideal for agriculture.
-
Great Plains: Stretching from Canada to Texas, the Great Plains are essential for the US agricultural economy. They are primarily used for growing wheat, corn, and other grains, earning the region the nickname "America's Breadbasket."
[Image of the Great Plains] Caption: Expansive wheat fields in the Great Plains, showcasing the region's agricultural significance. Alt text: Great Plains
-
Coastal Plains: Along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts, coastal plains provide a low-lying, relatively flat landscape. These areas are home to many major cities, including New York, Miami, and Houston. They are also important for fishing, tourism, and shipping.
The Mighty Rivers: Carving the Physical Map of US
Rivers are crucial components of the US physical map, serving as transportation routes, sources of water, and natural boundaries.
-
Mississippi River: The "Father of Waters," the Mississippi River is the longest river in North America. It drains a vast area of the central US, flowing from Minnesota to the Gulf of Mexico. It's a major transportation route for goods and connects many important agricultural and industrial centers.
[Image of the Mississippi River] Caption: The mighty Mississippi River flowing through the heartland of America. Alt text: Mississippi River
-
Missouri River: A major tributary of the Mississippi, the Missouri River also plays a vital role in the agricultural economy of the Great Plains.
-
Colorado River: Carving its way through the Grand Canyon, the Colorado River is a critical source of water for the southwestern US. However, its water resources are increasingly strained due to growing demand and drought.
-
Columbia River: Located in the Pacific Northwest, the Columbia River is essential for hydroelectric power generation and salmon fishing.
Deserts and Other Landform: Enriching the Physical Map of US
Beyond mountains, plains and rivers, the US Physical map also includes vast deserts such as the Mojave and Sonoran Deserts.
- Mojave and Sonoran Deserts: Characterized by extreme dryness and unique flora and fauna, the Mojave Desert (home to Death Valley) and the Sonoran Desert (known for its saguaro cacti) add another layer of diversity to the US landscape.
[Image of the desert landscape] Caption: Arid landscape of the Mojave Desert, showcasing its harsh beauty. Alt text: Mojave Desert
The Great Lakes: Shaping the Physical Map of US
The Great Lakes, located in the north-central US, are the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total area. They are a crucial source of freshwater, transportation route, and recreational area.
- Significance: The Great Lakes - Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario - are interconnected and drain into the Atlantic Ocean via the St. Lawrence River. They support a significant shipping industry and provide drinking water for millions of people.
Coastal Features: The Edge of the Physical Map of US
The US coastline is extensive and varied, encompassing sandy beaches, rocky cliffs, and marshy wetlands.
-
Atlantic Coast: Characterized by barrier islands, estuaries, and numerous bays, the Atlantic coast is densely populated and supports a vibrant tourism industry.
-
Pacific Coast: The Pacific coast features rugged cliffs, rocky beaches, and dramatic landscapes. The iconic California coastline is a prime example.
-
Gulf Coast: The Gulf Coast is known for its sandy beaches, warm waters, and extensive wetlands. It's a popular destination for recreation and tourism.
Impacts of Physical Geography on the US: The Interconnected Physical Map of US
The physical geography of the US has profoundly impacted its history, economy, and culture.
-
Agriculture: The fertile soil of the Great Plains has made the US a global agricultural powerhouse.
-
Transportation: Rivers and coastlines have facilitated trade and transportation, shaping the growth of cities and industries.
-
Climate: Mountain ranges influence precipitation patterns and create diverse climate zones across the country.
-
Tourism: National parks and scenic landscapes attract millions of visitors each year, boosting local economies.
The Future of US Physical Geography: The Evolving Physical Map of US
Climate change, population growth, and resource depletion are all impacting the US physical landscape. Understanding these challenges is crucial for sustainable management and conservation.
-
Climate Change: Rising sea levels, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and changes in precipitation patterns pose significant threats to coastal communities and ecosystems.
-
Resource Management: Water scarcity in the western US, soil erosion in agricultural areas, and deforestation are ongoing challenges that require careful management.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Physical Map of US
The physical map of the US is a testament to its diverse and dynamic landscape. From towering mountains to expansive plains, from mighty rivers to scenic coastlines, the US offers a wealth of natural beauty and resources. Understanding the physical geography of the US is essential for appreciating its history, economy, and future challenges.
Keywords: Physical map of US, United States geography, Appalachian Mountains, Rocky Mountains, Great Plains, Mississippi River, Colorado River, Great Lakes, US coastline, American landscape, USA physical features, US topography, America's Breadbasket.
Summary Question and Answer:
- Question: What are the two major mountain ranges in the US?
- Answer: The Appalachian Mountains and the Rocky Mountains.















Future Map Of America 2025 Nadya Verena BRM4346 Scallion Future Map United States Lowres Scaled Printable Physical Map Of The United States Map Of The United States 231eb4f49ab7276f317b4b0b44ecc2bf United States Map And Satellite Image 54 OFF Usa Physical Map Usa Map With Physical Features United States Map Usa Physical Map 125 Printable Physical Map Of The Us Printable Map Of The US Usa Physical Map United States 184214 High Detailed United States Of America Physical Map With Labeling Stock High Detailed United States Of America Physical Map With Labeling 2PGD9M9
Us Map In 2025 Brear Peggie 90Geographical Map Of USA USA Geographical Map Geographical Usa Map Physical Map Of The Us Labeled Physical Us Map Printable Physical Map Of The United States Map Of The United States 6223d6d5fe196d866c8a958ae65c6809 Physical Map USA Printable Map Of USA Usa Physical Wall Map By Geonova 1 Physical Map Usa Cdd827997e7c34d5d44db3e55418c95b United States Of America Physical Map Stock Vector High Detailed United States Of America Physical Map With Labeling 254562217
Physical Maps Stock Vector High Detailed North America Physical Map With Labeling 228959392 Physical Map Of The Us Labeled Usa Map Physical 1 Wissen Ber Eine Physische Karte Physical Map 8 Unlocking The Geography Of The United States A Comprehensive Guide To Us Geography Map Your Daily Printable Needs Printablee Com Physical Map Of Usn 17969 Map Of Us In 2025 Emma Norina USA Th Ng Tin B N N C M N M 2025 Map Of USA Physical Us Map Physical Map USA Printable Map Of USA Usa Detailed Physical Map N O W 1
Physical Map Of The United States Of America 638e6f5babeac2204c3e89d49787f0be Physical Map Of The United States Elevation Rivers And Landforms Physical Map Of United States Thumb United States Map Physical United States Map Physical United States Physical Map High Detailed United States Of America Physical Map 2PGD933 The Physical Map Of United States Of America Reveals Varied Relief The Physical Map Of United States Of America Reveals Varied Relief Including Plains Plains Rainforests And Major Rivers 2R4FWMP Physical Map Of The United States Mary W Tinsley Stock Vector High Detailed United States Of America Physical Map With Labeling 392033755 Future Map Of America 2025 Nadya Verena BRM4343 Scallion Future Map North America Text Right 2112x3000
Map Of America In 2025 Vita Aloysia Redone The Second American Civil War 2025 2033 V0 Oo1ijpvgnadc1 Physical Map Of USA United States Physical Map Whereig Com Usa Physical Map Exploring The Physical Map Of Us A Guide To Understanding The Terrain Usa Physical Map

